Understanding the Risks: Can Oral Sex Cause Disease?
Oral sex is often considered a safer alternative to other sexual activities, but many people wonder, can oral sex cause disease? The truth is that while oral sex carries lower risk for some infections compared to vaginal or anal sex, it is not risk-free. Many sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can be passed through oral-genital contact, and understanding these risks is essential for protecting your health.
How Infections Spread Through Oral Sex
Oral sex involves contact between the mouth and the genitals, anus, or sometimes other body parts. This contact creates a pathway for viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens to transfer from one person to another. The moist environment of the mouth, combined with small cuts or sores that may go unnoticed, can allow infections to enter the bloodstream or mucous membranes.
Common Sexually Transmitted Infections Transmitted Orally
1. Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): Oral herpes (cold sores) can be passed to the genital area and vice versa through oral sex. Many carriers don’t have visible sores but can still transmit the virus.
2. Human Papillomavirus (HPV): This virus can infect the mouth and throat and has been linked to certain cancers such as oropharyngeal cancer. HPV transmission through oral sex is a growing concern.
3. Gonorrhea: Oral gonorrhea can infect the throat, often without symptoms, but can cause sore throat and spread to others.
4. Chlamydia: Though less common, chlamydia can infect the throat through oral sex and may lead to complications if untreated.
5. Syphilis: This infection can be transmitted through contact with syphilis sores during oral sex.
6. HIV: While oral sex carries a lower risk for HIV transmission than other sexual activities, it is still possible, especially if there are open sores or bleeding gums.
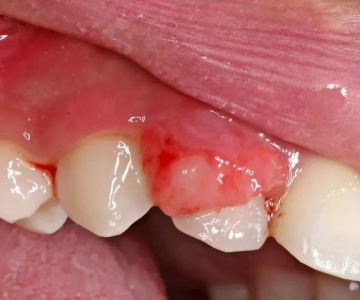
Oral Health’s Role in Disease Transmission
Your oral health significantly impacts the risk of disease transmission during oral sex. Conditions such as gum disease, bleeding gums, or mouth ulcers increase vulnerability to infections. Maintaining good dental hygiene and regular dental check-ups can reduce these risks substantially.
Personal Stories Highlighting Real Risks
Jessica, a 29-year-old from New York, shared her experience: “I never thought oral sex could be risky until I tested positive for oral gonorrhea after a routine screening. I didn’t have symptoms, which made me realize how important it is to talk openly about these risks and get tested regularly.”
Her story reflects a common reality—many STIs transmitted through oral sex go unnoticed without symptoms, making prevention and screening crucial.
Practical Tips to Stay Safe During Oral Sex
1. Use Barriers Consistently
Dental dams and condoms provide effective protection by creating a physical barrier that reduces contact with bodily fluids. Using these barriers every time during oral sex dramatically lowers the risk of STI transmission.
2. Communicate Openly with Partners
Discuss STI testing history, sexual health status, and boundaries before engaging in oral sex. Open communication builds trust and helps manage risks.
3. Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene
Brushing and flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly, can prevent gum disease and other oral conditions that increase infection risks.
4. Avoid Oral Sex with Open Sores or Infections
If you or your partner have cold sores, cuts, or any mouth infections, it’s best to wait until they heal to reduce the chance of transmission.
5. Regular STI Screenings
Routine testing is vital because many oral STIs are asymptomatic. Screening allows early detection and treatment, preventing further spread and complications.
Scientific Insights on Oral Sex and Disease Transmission
Recent studies show that oral sex is a significant route for transmission of several STIs, especially HPV. The rise of oropharyngeal cancers linked to HPV has heightened public health awareness. Healthcare providers increasingly recommend vaccination against HPV as an effective prevention method.
Moreover, ongoing research emphasizes the importance of barrier methods during oral sex, debunking myths that it is completely risk-free. These findings reinforce the message that knowledge and precaution are key to sexual health.
Role of HPV Vaccination
The HPV vaccine protects against the strains most commonly linked to cancer and genital warts. It is recommended for preteens and adults up to age 45. Vaccination not only protects against cervical cancer but also reduces oral HPV infections, making it a vital tool in reducing oral sex-related risks.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
If you experience unusual symptoms after oral sex—such as sores, persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or swollen glands—it’s important to seek medical advice promptly. Early diagnosis of oral STIs improves treatment outcomes and prevents transmission.
Additionally, regular sexual health check-ups allow healthcare professionals to provide personalized advice and screening tailored to your lifestyle.
Empowering Yourself with Knowledge and Care
Understanding can oral sex cause disease is the first step in making informed decisions about your sexual health. By recognizing the risks, practicing safe behaviors, and maintaining open communication, you can protect yourself and your partners effectively.
For those seeking comprehensive dental and sexual health advice, visiting a trusted provider like Dentistry Toothtruth offers access to professional guidance and tailored services. Their expert team can help you navigate prevention strategies and care options that suit your needs.



 White Bear Dentists4.0 (307 review)
White Bear Dentists4.0 (307 review) Dr Stein Dental Group4.0 (226 review)
Dr Stein Dental Group4.0 (226 review) Duncan Dental5.0 (344 review)
Duncan Dental5.0 (344 review) Pediatric Dental Associates of Philadelphia - Allegheny Ave4.0 (2097 review)
Pediatric Dental Associates of Philadelphia - Allegheny Ave4.0 (2097 review) Central Park Dental4.0 (519 review)
Central Park Dental4.0 (519 review) The Centre For Integrative Orthodontics4.0 (33 review)
The Centre For Integrative Orthodontics4.0 (33 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile