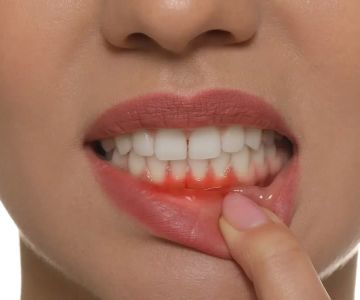
Causes of Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums can be caused by a buildup of dental plaque, which leads to gingivitis, periodontitis, and other gum diseases. Poor oral hygiene, smoking, and teeth grinding are common contributors. Additionally, underlying health conditions such as diabetes, hormone fluctuations, vitamin deficiencies, blood-clotting disorders, and even stress can cause your gums to bleed.
Care and Treatment Options
The treatment for bleeding gums depends on the underlying cause. If gum disease is the culprit, dentists or periodontists may recommend improved oral hygiene, antibiotics, tooth scaling and root planing, osseous surgery, or laser periodontal surgery. If the bleeding is not due to gum disease, healthcare providers may conduct tests to determine if conditions like diabetes, blood-clotting disorders, or vitamin deficiencies are the cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
Home Remedies and Precautions
If you have bleeding gums that don't improve within two weeks, it's advisable to schedule an appointment with a dentist. In the meantime, you can try brushing your teeth two to three times a day, flossing once daily, using a soft-bristled toothbrush, rinsing your mouth with warm saltwater, and using an antibacterial mouthwash. Avoid smoking as it can exacerbate the problem.
Ignoring Bleeding Gums
Ignoring bleeding gums can lead to worsening conditions. If gum disease is the cause, it can erode the tissue, ligaments, and bone supporting your teeth, causing a cycle of infection, bad breath, and even tooth loss. If another health issue is the culprit, your symptoms may worsen as the underlying condition progresses. It's crucial to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Prevention of Bleeding Gums
In many cases, bleeding gums due to gum disease can be prevented by visiting your dentist regularly and maintaining good oral hygiene at home. However, some causes like hormone changes, blood-clotting disorders, or leukemia may not be preventable.
When to See a Doctor
Bleeding gums may resolve on their own, but if the bleeding persists for more than two weeks, it's time to consult a dentist or primary care physician. They will either recommend treatment for bleeding gums or for an underlying condition.
Common Questions and Answers
Deficiencies of vitamins C and K can cause bleeding gums. You should be concerned about bleeding gums if they occur randomly or persist for longer than two weeks, accompanied by other symptoms like bad breath or swollen gums. While having bleeding gums is usually not an emergency, it's important to seek medical advice if the symptoms persist for more than two weeks.
In conclusion, bleeding gums can be a sign of various oral and systemic health issues. Understanding the causes, seeking appropriate treatment, and taking preventive measures are essential for maintaining healthy gums and overall well-being. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices can go a long way in preventing and addressing bleeding gums. If you experience persistent or concerning gum bleeding, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough assessment and personalized advice.





 Northside Dental Co.4.0 (457 review)
Northside Dental Co.4.0 (457 review) Dr. Jose Gallegos, DDS5.0 (122 review)
Dr. Jose Gallegos, DDS5.0 (122 review) Comfort Dental Raytown4.0 (162 review)
Comfort Dental Raytown4.0 (162 review) Kids Dental Land4.0 (602 review)
Kids Dental Land4.0 (602 review) Robert B Larson, LPN, JD - Dental Attorney4.0 (5 review)
Robert B Larson, LPN, JD - Dental Attorney4.0 (5 review) Meadows Dental Care4.0 (277 review)
Meadows Dental Care4.0 (277 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile