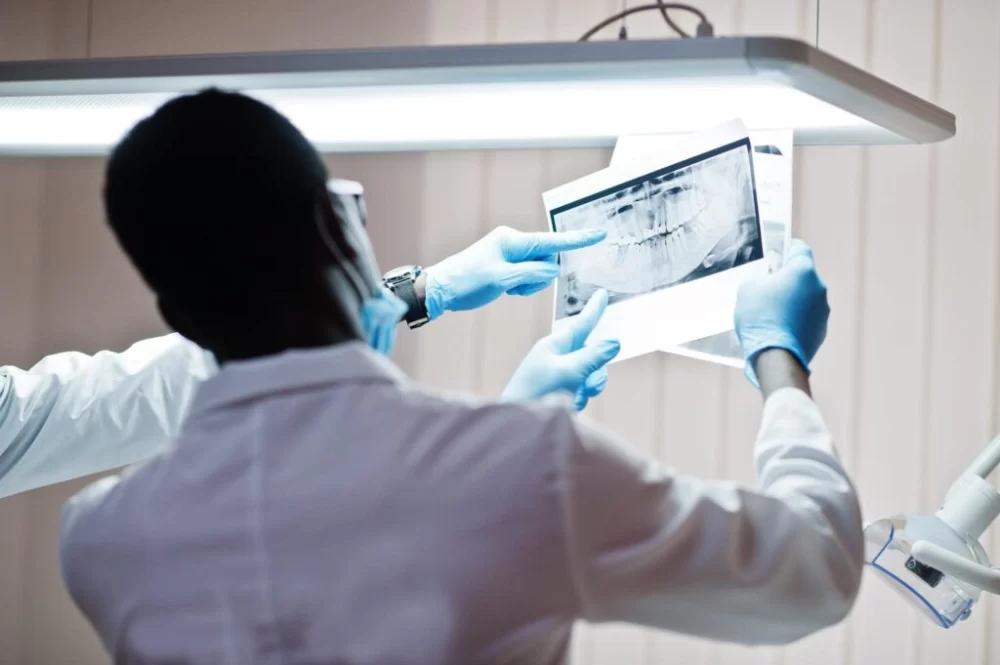
What Is the Definition of Oral Disease?
The term oral disease refers to any condition that affects the mouth, teeth, gums, or related structures. It encompasses a broad spectrum of disorders ranging from mild infections and inflammations to severe, chronic conditions that can impact overall health. Oral diseases are a major health concern worldwide and can affect people of all ages, often leading to pain, discomfort, and difficulties in eating, speaking, and social interaction.
1. Exploring the Scope of Oral Diseases
Oral diseases include various conditions such as dental caries (tooth decay), gingivitis, periodontitis, oral cancer, and infections like oral thrush. They may involve the teeth, gums, tongue, cheeks, roof and floor of the mouth, salivary glands, or jawbone. Each type of oral disease has unique causes, symptoms, and treatment methods, but all share the common trait of affecting the health and function of the mouth.
2. Causes and Risk Factors Behind Oral Diseases
Understanding why oral diseases develop helps in preventing and managing them effectively. The main causes include poor oral hygiene, tobacco use, unhealthy diet, genetic predisposition, and systemic health conditions such as diabetes. Bacteria buildup from plaque, viruses, fungi, and environmental factors also play significant roles.
For example, dental caries arise when bacteria produce acids that erode tooth enamel, often fueled by sugary foods and inadequate brushing. Gum diseases like gingivitis and periodontitis result from persistent plaque irritating the gums, causing inflammation and possible tissue damage. Oral cancer, on the other hand, may be linked to tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain viral infections.
3. The Impact of Oral Disease on Overall Health
Oral diseases are not just localized issues; they can have far-reaching consequences on general health. Studies have shown links between periodontitis and heart disease, stroke, diabetes complications, and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Chronic inflammation in the mouth can contribute to systemic inflammation, weakening the body's defenses and exacerbating other medical conditions.
4. Recognizing Symptoms and Seeking Early Diagnosis
Identifying signs of oral disease early can prevent severe damage. Common symptoms include persistent bad breath, bleeding or swollen gums, tooth sensitivity or pain, ulcers or sores that don’t heal, and changes in mouth tissue color. For instance, an early-stage gum disease might only cause mild redness and bleeding, but if untreated, it can progress to severe periodontitis causing tooth loss.
John’s story is a prime example: despite maintaining basic brushing habits, he noticed bleeding gums and persistent discomfort. A dentist’s evaluation revealed early periodontitis, which was treated successfully with professional cleaning and improved home care.
5. Prevention and Treatment Strategies
Good oral hygiene remains the cornerstone of preventing oral diseases. This includes brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings. Beyond hygiene, avoiding tobacco products, moderating sugary foods, and maintaining a balanced diet support oral health.
When oral disease occurs, treatment varies from simple interventions like fillings and cleanings to more complex procedures such as root canals, periodontal therapy, or surgery. Early detection significantly improves outcomes.
6. The Role of Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about oral diseases helps reduce their prevalence. Educational campaigns encourage people to recognize risk factors and symptoms, promoting healthier habits. Access to affordable dental care and services like those provided by Dentistry Toothtruth ensures timely intervention, enhancing community oral health.
Oral Disease: A Comprehensive Understanding for Better Health
In summary, oral disease covers a wide range of conditions impacting the mouth and related structures. Knowing the definition, causes, symptoms, and prevention techniques empowers individuals to maintain healthy smiles and improve their quality of life. For personalized guidance and effective treatment options, visit Dentistry Toothtruth, your trusted partner in oral health care.



 Professional Endodontics of Illinois4.0 (68 review)
Professional Endodontics of Illinois4.0 (68 review) Honey Creek Dental4.0 (58 review)
Honey Creek Dental4.0 (58 review) Pediatric Dental Associates of Randolph4.0 (1772 review)
Pediatric Dental Associates of Randolph4.0 (1772 review) Bensalem Dental Specialties Center3.0 (162 review)
Bensalem Dental Specialties Center3.0 (162 review) George Orthodontics4.0 (55 review)
George Orthodontics4.0 (55 review) Northside Dental Clinic4.0 (281 review)
Northside Dental Clinic4.0 (281 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile