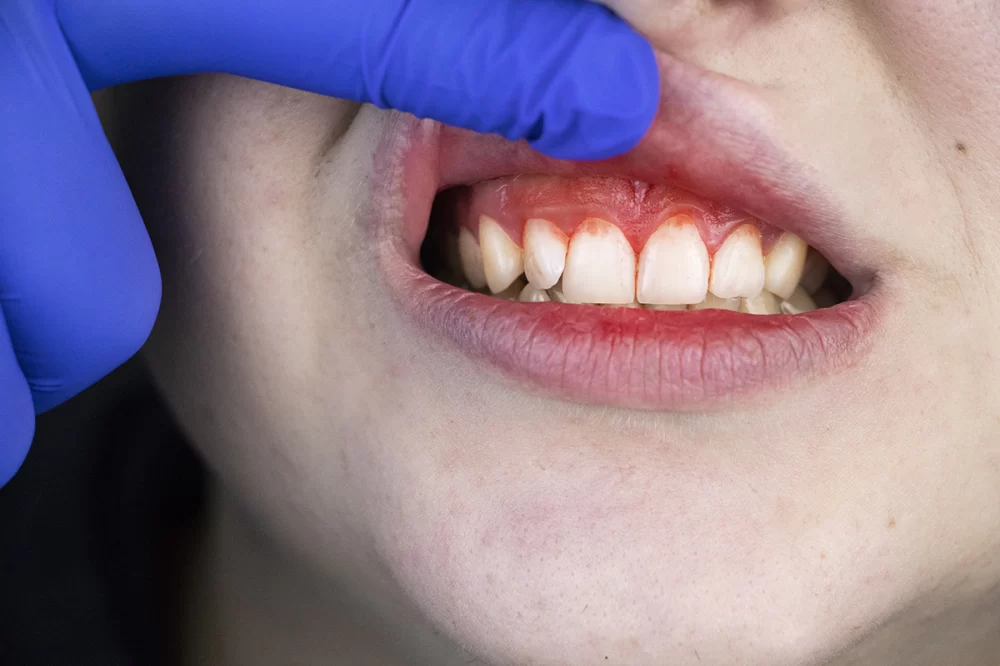
What Are the Signs of Gingivitis?
- 1. Early Signs of Gingivitis
- 2. More Severe Symptoms of Gingivitis
- 3. Treatment Options for Gingivitis
- 4. Prevention Tips for Gingivitis
1. Early Signs of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease that causes irritation, redness, and swelling (inflammation) of your gums. It’s important to catch gingivitis early, as it can be reversed with good oral hygiene. Here are the early signs of gingivitis:
1.1 Red or Swollen Gums
One of the first signs of gingivitis is that your gums will appear redder than usual. They might also become swollen and feel soft to the touch. Healthy gums are typically light pink, firm, and do not bleed easily. If you notice that your gums look swollen or darker in color, it’s time to pay closer attention.
1.2 Bleeding Gums
Another early sign of gingivitis is bleeding gums, especially after brushing or flossing. This is often a clear indication that plaque has built up along the gum line, causing irritation. Although bleeding gums are common during the early stages of gingivitis, they should not be ignored, as they can develop into a more serious problem if left untreated.
1.3 Bad Breath
Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth can be another indicator of gingivitis. The buildup of plaque and bacteria around the gums can cause unpleasant odors. If you find that your breath remains bad despite regular brushing, it could be a sign that gingivitis is beginning to develop.
2. More Severe Symptoms of Gingivitis
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress into more severe forms of gum disease, such as periodontitis. The following are symptoms that indicate gingivitis may be advancing:
2.1 Painful Gums
As gingivitis worsens, your gums might become more painful and sensitive, especially when eating hot, cold, or spicy foods. If the pain persists or worsens, this could be a sign that the condition is progressing into periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss if not addressed quickly.
2.2 Receding Gums
Another more severe symptom is the recession of the gums. Receding gums expose more of the tooth, creating pockets that can trap bacteria and plaque. This can lead to further gum damage, loosening of the teeth, and an increased risk of more serious oral health problems.
2.3 Pus Between Teeth and Gums
When gingivitis becomes severe, pus may form between your teeth and gums, which is an indication of an infection. This is a serious sign that you need to visit a dentist as soon as possible. Pus is a common symptom of advanced gum disease and requires immediate treatment.
3. Treatment Options for Gingivitis
Luckily, gingivitis is usually reversible with proper treatment. Here are some effective treatments to help restore your gum health:
3.1 Professional Cleaning
A visit to your dentist for a professional cleaning is essential for removing plaque and tartar buildup that regular brushing cannot remove. A dentist can deep clean your teeth, including below the gum line, to prevent further complications.
3.2 Improved Oral Hygiene
Maintaining good oral hygiene is key to treating gingivitis. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily to remove food particles and plaque, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash to help reduce bacteria.
3.3 Antibacterial Treatment
In some cases, your dentist may recommend an antibacterial mouth rinse or a medicated treatment to help reduce bacteria and plaque in your mouth. These treatments can help speed up the healing process and prevent the progression of gingivitis.
4. Prevention Tips for Gingivitis
While gingivitis is common, it’s also preventable. Follow these tips to keep your gums healthy and reduce the risk of gingivitis:
4.1 Brush and Floss Regularly
Brushing and flossing are the most effective ways to prevent gingivitis. Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque that can build up along the gum line. This simple habit is the foundation of good oral health.
4.2 Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Regular dental checkups are crucial for maintaining gum health. Your dentist can catch early signs of gingivitis before they become serious, provide professional cleanings, and offer tailored advice for your oral care routine.
4.3 Use Mouthwash
Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in the mouth and freshen your breath. Choose a mouthwash that is proven to fight plaque and gingivitis for an added layer of protection against gum disease.







 Noll Family Dentistry4.0 (95 review)
Noll Family Dentistry4.0 (95 review) Dr. David R. Resch DDS0.0 (0 review)
Dr. David R. Resch DDS0.0 (0 review) Decatur Orthodontics5.0 (379 review)
Decatur Orthodontics5.0 (379 review) Reynolds, Clinton DDS5.0 (24 review)
Reynolds, Clinton DDS5.0 (24 review) Gentle Dental Rio Vista4.0 (152 review)
Gentle Dental Rio Vista4.0 (152 review) Little Big Smiles Pediatric Dentistry of Fort Myers5.0 (130 review)
Little Big Smiles Pediatric Dentistry of Fort Myers5.0 (130 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile