- Understanding Tooth Decay
- Causes of Tooth Decay
- Signs of Tooth Decay and Sensitivity
- Tooth Sensitivity: Causes and Remedies
- How to Prevent Tooth Decay and Sensitivity
- Case Studies: Real-Life Experiences with Tooth Decay
- Effective Solutions and Treatments for Tooth Decay and Sensitivity
Understanding Tooth Decay
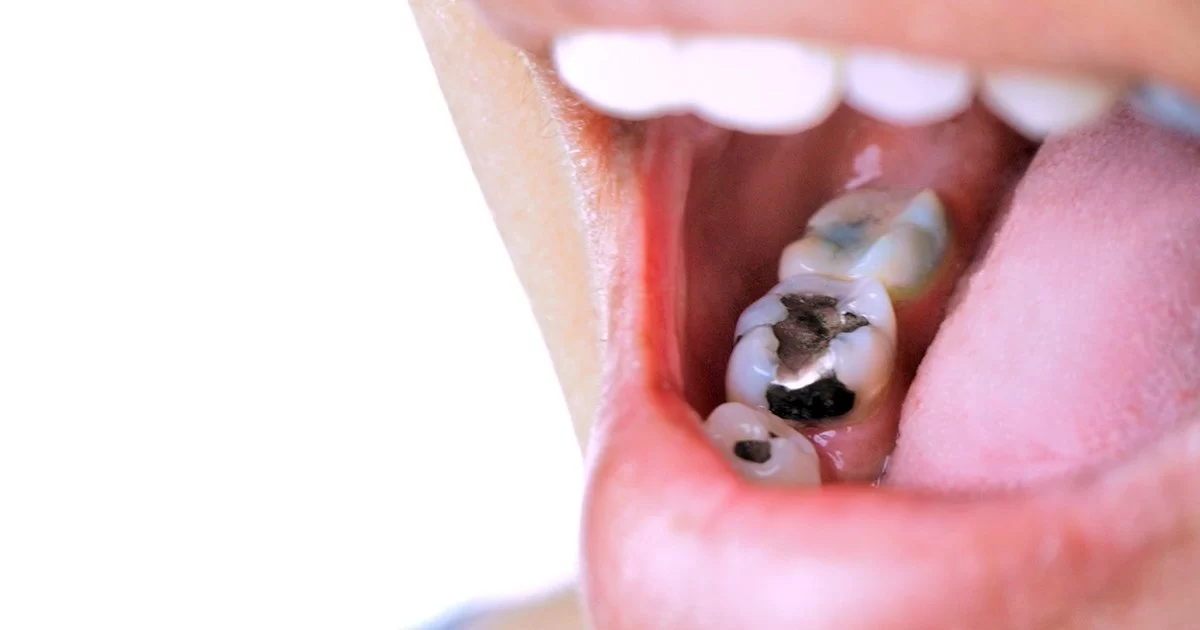
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, is a common issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the enamel, the hard outer surface of a tooth, is damaged by acids produced by bacteria in your mouth. These acids break down the enamel, leading to cavities and further damage if left untreated. Tooth decay is not only painful but can also result in tooth loss if not addressed early.
In addition to causing visible damage, tooth decay can also contribute to tooth sensitivity, making it difficult to eat or drink hot and cold foods without discomfort. Understanding how tooth decay and tooth sensitivity issues are connected can help you take proactive steps to protect your teeth and overall oral health.
Causes of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is primarily caused by a combination of factors, including poor oral hygiene, diet, and genetics. The most common causes include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Not brushing and flossing your teeth regularly allows plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to form on your teeth, which produces acids that contribute to decay.
- Diet High in Sugars and Acids: Consuming sugary foods and beverages provides fuel for the bacteria that cause tooth decay. Additionally, acidic foods and drinks can erode enamel over time.
- Dry Mouth: A lack of saliva, which helps wash away food particles and neutralize acids, can make you more susceptible to tooth decay.
- Genetics: Some people may be more prone to tooth decay due to factors such as weaker enamel or saliva composition.
Signs of Tooth Decay and Sensitivity
Tooth decay can be difficult to detect in its early stages, but there are several common signs to watch for:
- Pain when Eating or Drinking: Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods is one of the first signs of tooth decay.
- Visible Holes or Pits in Teeth: As decay progresses, cavities may become visible on the surface of the tooth.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath or a foul taste in your mouth can be a result of bacteria from decaying teeth.
- Tooth Discoloration: Teeth may appear darker, especially if decay is present beneath the enamel.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to visit your dentist promptly to prevent further damage.
Tooth Sensitivity: Causes and Remedies
Tooth sensitivity often goes hand in hand with tooth decay, as the enamel is worn down and the underlying layers of the tooth are exposed. This can lead to discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or acidic foods. The causes of tooth sensitivity include:
- Gum Recession: As gums recede, the sensitive root areas of your teeth may be exposed, causing discomfort.
- Enamel Erosion: Wear and tear on tooth enamel from brushing too hard, consuming acidic foods, or grinding your teeth can make teeth more sensitive.
- Tooth Decay: As decay progresses and the tooth structure weakens, sensitivity can occur due to nerve exposure.
Fortunately, there are remedies for tooth sensitivity, such as using desensitizing toothpaste, avoiding acidic foods, and using a soft-bristled toothbrush.
How to Prevent Tooth Decay and Sensitivity
Preventing tooth decay and sensitivity starts with good oral hygiene practices. Here are a few tips to keep your teeth healthy:
- Brush Twice a Day: Use fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean your teeth twice daily. Don't forget to brush your tongue, too!
- Floss Daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles between teeth, helping to prevent decay.
- Limit Sugary and Acidic Foods: Reduce your intake of sugary snacks and acidic drinks, and rinse your mouth with water after consuming them.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Regular checkups and cleanings allow your dentist to catch and treat problems early, preventing more serious issues like cavities and gum disease.
Case Studies: Real-Life Experiences with Tooth Decay
Sarah, a 32-year-old woman, had been experiencing tooth sensitivity for months before visiting her dentist. After a thorough examination, her dentist discovered several cavities and explained that her sensitivity was caused by enamel erosion from acidic foods. After receiving treatment for the cavities and switching to a toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth, Sarah's discomfort was greatly reduced.
John, a 45-year-old man, had ignored his tooth sensitivity for years. His dentist discovered that the problem was caused by untreated tooth decay. After undergoing restorative treatments, including fillings and fluoride treatments, John was able to return to eating his favorite foods without discomfort.
Effective Solutions and Treatments for Tooth Decay and Sensitivity
If you’re already dealing with tooth decay or sensitivity, several treatment options are available to help restore your oral health:
- Fillings and Restorations: If decay has caused a cavity, your dentist can clean the area and fill the hole with a material like composite resin or amalgam.
- Fluoride Treatments: Fluoride helps to strengthen enamel and can reduce sensitivity.
- Desensitizing Toothpaste: Special toothpaste formulations can help block pain signals and reduce tooth sensitivity.
- Root Canals: In severe cases of decay, a root canal may be necessary to remove infected tissue and restore the tooth’s function.
If you're experiencing tooth decay or sensitivity issues, it's important to seek professional treatment early. You can learn more about preventive care and treatment options at Dentistry Toothtruth for personalized advice and solutions.







 Western Dental & Orthdontics Kids4.0 (394 review)
Western Dental & Orthdontics Kids4.0 (394 review) Southside Orthodontics - Your Colonial Heights and Chesterfield Orthodontist4.0 (274 review)
Southside Orthodontics - Your Colonial Heights and Chesterfield Orthodontist4.0 (274 review) Prosthodontic & Implant Associates5.0 (2 review)
Prosthodontic & Implant Associates5.0 (2 review) Neville Dental Care5.0 (46 review)
Neville Dental Care5.0 (46 review) The Smile Institute Advanced Dentistry & Orthodontics4.0 (256 review)
The Smile Institute Advanced Dentistry & Orthodontics4.0 (256 review) Calder Dental4.0 (5 review)
Calder Dental4.0 (5 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile