Understanding Gum Recession
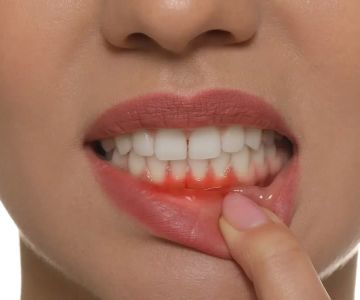
Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue around the teeth starts to pull away, exposing the roots. This can be caused by a multitude of factors such as aggressive brushing, smoking, periodontal disease, genetics, and more. Gum recession not only makes the teeth more vulnerable to cavities and sensitivity but can also lead to more serious oral health problems if left untreated.
Symptoms and Causes of Gum Recession
The most obvious symptom of gum recession is the exposure of tooth roots. Other signs include pain or discomfort near the gum line, sensitivity to heat, cold, and sweets, and sensitivity during brushing and flossing. The causes of gum recession can range from improper brushing techniques and tartar buildup to underlying health conditions and genetic predispositions.
Diagnosis and Tests for Gum Recession
Your dentist can diagnose gum recession during a routine examination by measuring the amount of gum recession and the depth of periodontal pockets. This helps determine the severity of the condition and the appropriate treatment plan.
Management and Treatment Approaches
While receding gums cannot grow back, various measures can be taken to prevent the condition from worsening. For instance, desensitizing agents and toothpaste can reduce sensitivity. The treatment options for gum recession depend on the underlying cause and severity. Nonsurgical treatments like topical antibiotics, dental bonding, and orthodontics may be effective for mild cases. However, gum graft surgery is often required for more severe gum recession.
Gum Graft Surgery
This is a common surgical procedure where a gum graft is used to replace the missing gum tissue. The graft is typically taken from the roof of the mouth or sometimes from sterilized human donor tissue. The recovery time after gum grafting surgery varies depending on several factors, but in most cases, patients feel back to normal within two weeks.
Prevention of Gum Recession
Although gum recession cannot always be prevented, especially if you have a genetic predisposition, you can significantly reduce the risk by maintaining proper oral hygiene. This includes thorough brushing twice a day, daily flossing, using an antimicrobial mouthwash, and following your dentist's recommendations for teeth cleanings. Avoiding smoking and using chewing tobacco is also crucial.
Outlook and Prognosis
If gum recession is detected early and treated promptly, the chances of successful management and prevention of further deterioration are higher. However, it's important to note that gum recession cannot be completely cured but can be managed effectively with the right treatment and care.
Living with Gum Recession
If you notice any signs of gum recession such as increased visibility of tooth roots or increased tooth sensitivity, it's essential to see your dentist or periodontist promptly. Asking the right questions during your dental visit can help you better understand your condition and the available treatment options.
Gum recession is a common oral health issue that requires attention and appropriate treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options, you can take proactive steps to protect your gum health and overall oral well-being. Whether it's through non-surgical measures, surgical procedures like gum grafting, or preventive practices, there are various ways to manage and potentially improve the condition of your gums. Remember, early detection and intervention are key to maintaining a healthy smile.





 Westwind Dental Tolleson4.0 (262 review)
Westwind Dental Tolleson4.0 (262 review) Plum Grove Dental Center: Thomas A. Harris, DDS5.0 (6 review)
Plum Grove Dental Center: Thomas A. Harris, DDS5.0 (6 review) Smile Central Dental4.0 (506 review)
Smile Central Dental4.0 (506 review) Southern Smiles Newnan5.0 (449 review)
Southern Smiles Newnan5.0 (449 review) Dr. David C. DiBenedetto, DMD4.0 (30 review)
Dr. David C. DiBenedetto, DMD4.0 (30 review) Pediatric Dental Associates of Philadelphia - Allegheny Ave4.0 (2097 review)
Pediatric Dental Associates of Philadelphia - Allegheny Ave4.0 (2097 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile