- Understanding-Oral-Fungal-Infections
- Symptoms-and-Causes
- Treatment-Options
- Natural-Remedies-and-Prevention
- Professional-Care-and-Recommendations
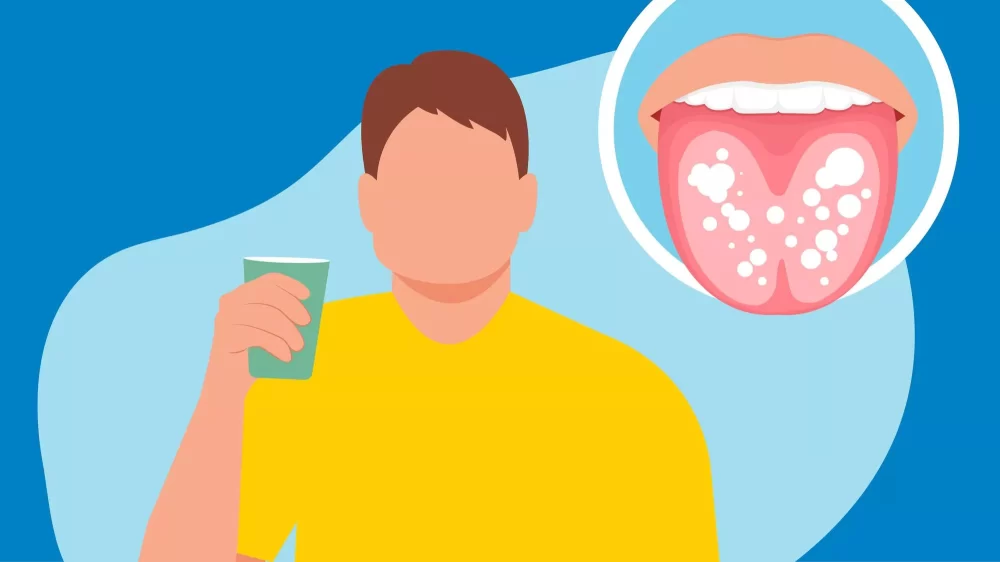
Understanding Oral Fungal Infections
Oral fungal infections, commonly known as oral thrush or candidiasis, occur when an overgrowth of Candida species disrupts the natural balance of microorganisms in the mouth. This imbalance often leads to white patches, soreness, and discomfort that affect eating, speaking, and overall oral health. Understanding how to treat oral fungal infections requires not only recognizing symptoms but also identifying underlying causes, which can range from weakened immunity to the use of antibiotics or inhaled steroids.
The Nature of Candida in the Mouth
Candida is a type of yeast naturally present in the mouth, digestive tract, and skin. Usually, it coexists harmlessly with other microbes. However, when the immune system is compromised or the oral environment changes, Candida can proliferate excessively, leading to infection. This condition is more prevalent among infants, the elderly, denture wearers, and individuals with diabetes or HIV.
Why Prompt Treatment Matters
If left untreated, oral fungal infections can worsen, causing pain, difficulty swallowing, and spreading to other parts of the body, especially in immunocompromised patients. Early treatment not only alleviates discomfort but also prevents complications. For anyone wondering how to treat oral fungal infections effectively, a clear understanding of symptoms and treatment paths is essential.
Symptoms and Causes
Recognizing the symptoms of oral fungal infections is the first step toward effective treatment. Common signs include creamy white lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, roof of the mouth, gums, and tonsils. These patches may bleed if scraped and can cause burning sensations or a cottony feeling in the mouth.
Identifying Common Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of oral fungal infections:
- Antibiotic Use: Disrupts the balance of bacteria that normally control Candida growth.
- Immune Suppression: Conditions like HIV/AIDS, cancer treatments, or corticosteroid medications weaken the immune defense.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Can foster an environment for fungal overgrowth, especially with ill-fitting dentures.
- Underlying Health Issues: Diabetes and dry mouth conditions reduce natural defenses.
Case Insight: The Story of Jane
Jane, a 62-year-old denture wearer with type 2 diabetes, experienced persistent white patches and discomfort. Her condition worsened until she consulted her dentist, who diagnosed oral thrush. Through a combination of antifungal medication and improved denture hygiene, Jane’s symptoms resolved within weeks. Her case highlights the importance of managing predisposing factors in treating oral fungal infections.
Treatment Options
How to treat oral fungal infections effectively depends on severity, patient health, and underlying causes. Treatments can be broadly categorized into medical interventions and supportive care.
Medical Treatments
The primary approach to treating oral fungal infections is antifungal therapy. These include:
- Topical Antifungals: Nystatin suspension or clotrimazole lozenges applied directly to the affected area to reduce yeast overgrowth.
- Systemic Antifungals: Oral fluconazole or itraconazole prescribed for more severe or persistent infections, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- Addressing Underlying Causes: Adjusting medications that may contribute to fungal growth or controlling systemic diseases like diabetes.
Importance of Compliance
Patients must complete the full course of antifungal treatment to prevent recurrence. Stopping medication too soon can cause the infection to return more resistant to therapy. Regular dental checkups during treatment help monitor progress and oral health status.
Natural Remedies and Prevention
While professional treatment is critical, natural remedies and preventive practices can support healing and reduce recurrence risk.
Effective Home Care Strategies
- Maintain Oral Hygiene: Brushing twice daily and flossing helps keep the mouth free from harmful microbes.
- Rinse with Saltwater: Warm saltwater rinses soothe irritation and help remove debris.
- Probiotics: Certain probiotics may help restore the natural microbial balance in the mouth.
- Dietary Adjustments: Reducing sugar intake limits the food source for Candida growth.
Real-Life Example: Mark’s Experience
Mark struggled with recurrent oral thrush linked to his frequent antibiotic use for respiratory infections. Alongside prescribed medication, he incorporated saltwater rinses and adjusted his diet. These measures, combined with recommendations from Dentistry Toothtruth, helped him achieve lasting relief and improve oral health resilience.
Professional Care and Recommendations
Consulting healthcare professionals ensures accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plans tailored to individual needs. Dentists and doctors can perform oral swabs or cultures to confirm fungal infection and rule out other conditions.
Why Choose Specialized Services?
Professional clinics like Dentistry Toothtruth offer comprehensive evaluations and access to advanced antifungal medications and oral care products. Their expertise helps manage complicated cases and provides personalized advice on hygiene, diet, and lifestyle modifications.
Optimizing Long-Term Oral Health
Beyond immediate treatment, maintaining a healthy oral environment prevents future infections. Regular dental visits, managing chronic conditions, and using recommended products are essential strategies recommended by dental professionals.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of oral fungal infections, consider reaching out to Dentistry Toothtruth to explore the best treatment options and oral care products available.







 OC Centers for Oral Surgery & Dental Implants - San Clemente5.0 (199 review)
OC Centers for Oral Surgery & Dental Implants - San Clemente5.0 (199 review) Family & Spa Dentistry4.0 (178 review)
Family & Spa Dentistry4.0 (178 review) Lowery Smiles5.0 (305 review)
Lowery Smiles5.0 (305 review) Avi Malkis, DDS5.0 (142 review)
Avi Malkis, DDS5.0 (142 review) Ling Family Dentistry4.0 (427 review)
Ling Family Dentistry4.0 (427 review) Adelante Healthcare3.0 (348 review)
Adelante Healthcare3.0 (348 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile