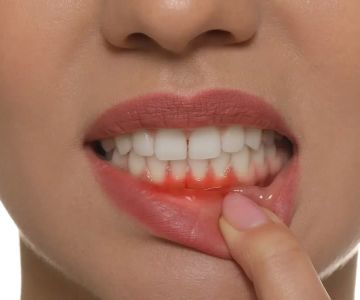
Causes of Gum Bleeding
Gum bleeding can result from multiple factors. Poor oral hygiene is a frequent culprit. Smoking, gingivitis (early-stage gum disease), and periodontitis (moderate to advanced gum disease) are common dental causes. Additionally, other conditions such as diabetes, hormone changes during puberty, pregnancy or menopause, vitamin K and C deficiencies, blood-thinning medications, pernicious anemia, thrombocytopenia, hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, oral herpes, HIV/AIDS, stress, and leukemia can also contribute to gum bleeding.
Treatment Options for Gum Bleeding
The treatment for gum bleeding depends on the underlying cause. If gum disease is the cause, dentists or periodontists might recommend improved oral hygiene at home, antibiotics, tooth scaling and root planing, osseous surgery, or laser periodontal surgery. For cases where gum disease isn't the issue, healthcare providers will conduct tests to determine if there are underlying health conditions like diabetes, blood-clotting disorders, or vitamin deficiencies and then recommend appropriate treatment.
Home Remedies and Precautions
To stop gum bleeding at home, it's recommended to brush two to three times a day, floss once daily, use a soft-bristled toothbrush, rinse the mouth with warm saltwater, and use an antibacterial mouthwash. Avoid smoking. Ignoring gum bleeding can lead to worsening conditions, especially if gum disease is the cause. Untreated gum disease can erode the supporting tissues, ligaments, and bone of the teeth, causing a cycle of infection, bad breath, and even tooth loss. If gum bleeding persists for more than two weeks, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider.
Common Questions and Answers
Vitamin C and K deficiencies can cause gum bleeding. If your gums randomly bleed without an obvious cause or if the bleeding lasts for more than two weeks, it's a cause for concern. It's not advisable to ignore gum bleeding for an extended period as it can worsen underlying conditions. In many cases, gum bleeding can be prevented by maintaining regular dental visits and practicing good oral hygiene at home, although some causes like hormone changes or certain diseases might not be preventable.
In conclusion, gum bleeding is not a minor issue and should be taken seriously. It can be a sign of gum disease or other underlying health conditions. Understanding the causes, seeking appropriate treatment, and adopting preventive measures are crucial for maintaining good oral health and overall well-being. Regular communication with healthcare providers and dentists is essential to address gum bleeding effectively and ensure a healthy mouth.





 Palm Valley Orthodontics5.0 (3 review)
Palm Valley Orthodontics5.0 (3 review) Valley View Dental4.0 (1195 review)
Valley View Dental4.0 (1195 review) Kellyn Hodges Orthodontics4.0 (301 review)
Kellyn Hodges Orthodontics4.0 (301 review) Dr. Joshua A. Bresler, DMD3.0 (5 review)
Dr. Joshua A. Bresler, DMD3.0 (5 review) Niver & Sobel5.0 (4 review)
Niver & Sobel5.0 (4 review) Leila Zamiri DDS - Cherry Office4.0 (134 review)
Leila Zamiri DDS - Cherry Office4.0 (134 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile