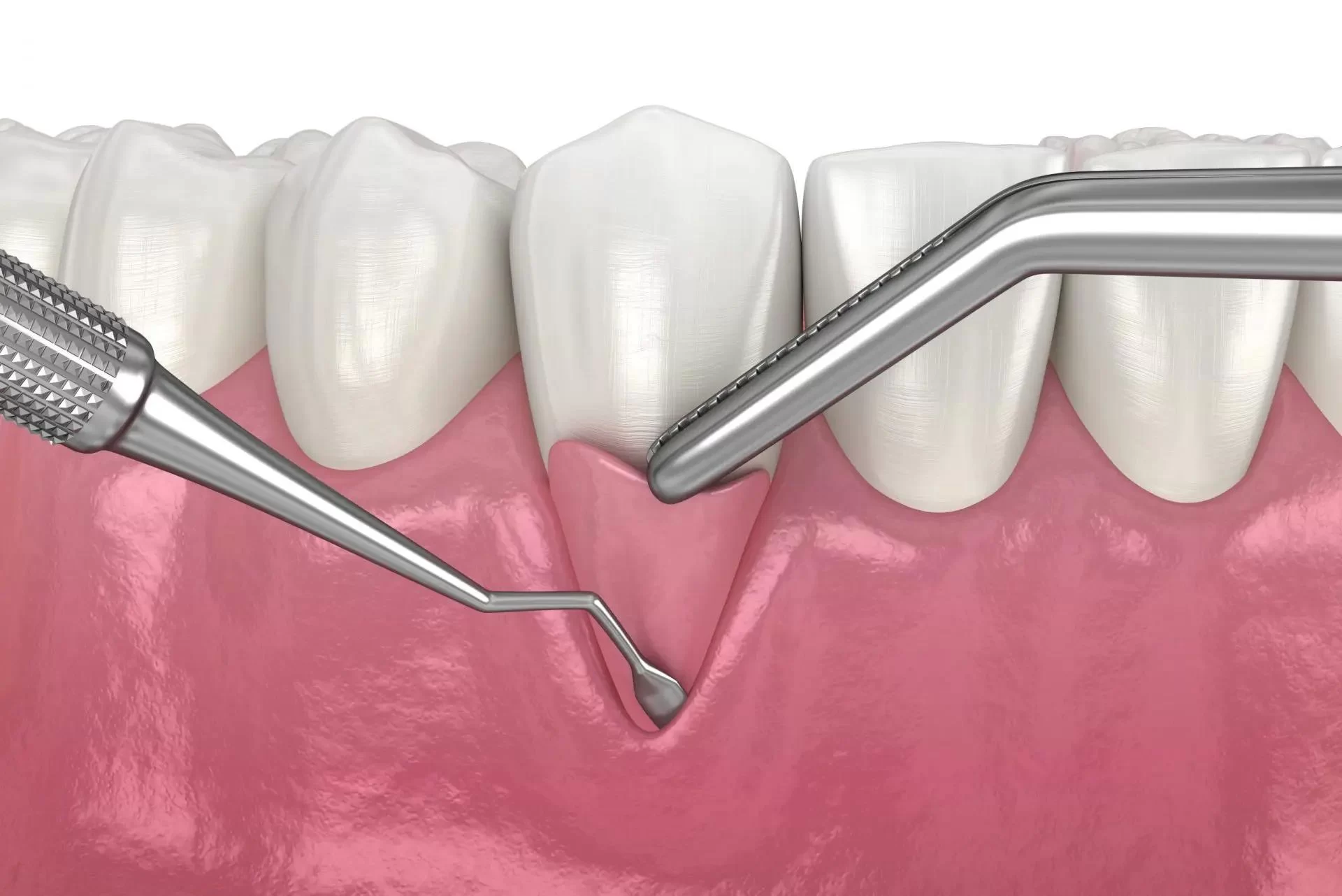
What is a Gingival Graft and When is It Needed? Understanding Gum Graft Surgery
- 1. What is a Gingival Graft?
- 2. Why is a Gingival Graft Needed?
- 3. When is a Gingival Graft Needed?
- 4. The Gingival Graft Procedure
- 5. Recovery After a Gingival Graft
- 6. Alternatives to Gingival Grafts
1. What is a Gingival Graft?
A gingival graft, also known as a gum graft, is a dental procedure used to treat gum recession. It involves taking tissue from one part of the mouth (usually the roof of the mouth) and grafting it onto the affected areas of the gums. The goal is to restore gum tissue that has been lost or worn down due to factors like gum disease, genetics, or aggressive brushing.
2. Why is a Gingival Graft Needed?
Gingival grafts are necessary to address the loss of gum tissue that can occur as a result of gum recession. When the gums recede, the roots of the teeth may become exposed, making them more vulnerable to decay, sensitivity, and further damage. A gingival graft helps to protect the teeth and restore a more natural gum line, improving both the function and appearance of your smile.
3. When is a Gingival Graft Needed?
There are several signs that may indicate the need for a gingival graft:
- Exposed Tooth Roots: If you notice that your tooth roots are becoming exposed, this is a clear sign of gum recession that may require a gingival graft.
- Increased Tooth Sensitivity: Gum recession can lead to heightened sensitivity, especially when eating hot or cold foods, which may signal the need for a graft.
- Cosmetic Concerns: If your gums have receded significantly, you may feel self-conscious about the appearance of your teeth and want to restore the gum line.
- Progressive Gum Recession: If your gum recession is getting worse over time, a gingival graft may be needed to stop it from progressing further.
If you experience any of these issues, it’s important to consult with a dentist to determine if a gingival graft is the right solution.
4. The Gingival Graft Procedure
The gingival graft procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Consultation and Examination: Your dentist will examine your gums and take x-rays to assess the extent of the recession.
- Graft Harvesting: A small amount of tissue is taken from the roof of your mouth or from a donor site to be used in the grafting process.
- Graft Placement: The harvested tissue is carefully placed on the areas of the gums that need to be repaired.
- Suturing: The graft is secured with stitches to ensure proper healing and attachment to the surrounding tissue.
While the procedure is generally performed under local anesthesia, in some cases, sedation may be used for patient comfort. It typically takes about 1-2 hours, depending on the extent of the procedure.
5. Recovery After a Gingival Graft
After the gingival graft procedure, you will need to follow specific aftercare instructions to ensure proper healing. These may include:
- Post-Operative Pain Management: Mild discomfort is common after the procedure, but your dentist will recommend pain relievers to manage this.
- Dietary Restrictions: For the first few days, you may need to avoid hard, crunchy foods and stick to a soft diet to prevent irritation to the graft site.
- Oral Hygiene: It’s crucial to avoid brushing the grafted area for a while to allow the tissue to heal. Your dentist will provide guidance on how to care for your teeth and gums during recovery.
Most patients can return to normal activities within a few days, but full healing may take several weeks. It's important to attend follow-up appointments to ensure the graft is healing properly.
6. Alternatives to Gingival Grafts
While a gingival graft is often the most effective solution for severe gum recession, there are some alternative treatments available:
- Scaling and Root Planing: For early stages of gum recession, deep cleaning may help remove plaque and tartar that contribute to the recession.
- Desensitizing Agents: If sensitivity is a primary concern, desensitizing toothpaste or other treatments may provide relief.
- Laser Therapy: Some dentists offer laser treatment to stimulate gum tissue growth and reduce recession without the need for a surgical graft.
Consult with your dentist to discuss which option is best suited to your needs and the severity of your gum recession.







 Bismarck Dentistry4.0 (44 review)
Bismarck Dentistry4.0 (44 review) Highland Dental Clinic: Dr. Robert Klein5.0 (7 review)
Highland Dental Clinic: Dr. Robert Klein5.0 (7 review) Baystate Family Dental4.0 (27 review)
Baystate Family Dental4.0 (27 review) Bright Now! Dental & Orthodontics4.0 (221 review)
Bright Now! Dental & Orthodontics4.0 (221 review) Georgetown Family Dentistry4.0 (359 review)
Georgetown Family Dentistry4.0 (359 review) Westlake Family Dentistry4.0 (155 review)
Westlake Family Dentistry4.0 (155 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile