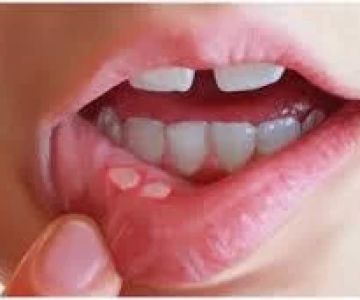
Oral ulcers, commonly known as mouth sores, are a prevalent health concern that affects many individuals at least once in their lifetime. These small but painful lesions can appear on the inside of the mouth, lips, or even the throat. While they often heal on their own, the duration and pain associated with them can vary significantly. For American readers experiencing recurrent oral ulcers, understanding whether these lesions heal autonomously or if they require medical intervention is crucial. This article explores the self-healing potential of oral ulcers and examines the risks associated with leaving them untreated.
The Self-Healing Nature of Oral Ulcers
Oral ulcers frequently resolve without medical treatment. Minor aphthous ulcers, for instance, typically heal within one to two weeks. These self-limiting sores are often triggered by minor injuries, stress, hormonal changes, or certain foods. The body's natural healing processes are usually capable of repairing the damaged mucosal tissue relatively quickly. However, while waiting for them to heal on their own, patients may experience discomfort that interferes with daily activities like eating and talking. Thus, managing symptoms with over-the-counter remedies or home care strategies is essential to improve quality of life during the healing process.
Potential Risks of Leaving Oral Ulcers Untreated
While many oral ulcers heal spontaneously, ignoring persistent or recurring sores can be risky. Long-standing ulcers may signify underlying health issues such as nutritional deficiencies, gastrointestinal diseases, or even oral cancer. In the United States, where oral health awareness is emphasized, addressing symptoms early can prevent potential complications. Untreated ulcers can also become infected, leading to increased pain and delayed healing. Therefore, if an ulcer persists beyond two weeks, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional to explore possible causes and appropriate treatments.
Effective Self-Care and Treatment Strategies
Managing oral ulcers requires a combination of home care practices and, occasionally, professional interventions. Simple measures like maintaining good oral hygiene, using antiseptic mouthwashes, and avoiding irritants can significantly accelerate healing. For recurrent ulcers, identifying and eliminating potential triggers—such as certain foods or stressors—is beneficial. In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe topical treatments like corticosteroid lozenges or gels. Ensuring an adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, particularly B vitamins, folate, and iron, is also essential in preventing ulcer formation.
When to Seek Professional Help
It is important to know when to seek advice from a dentist or a doctor for oral ulcers. Alarm signs include ulcers that do not heal in a timely manner, are exceptionally large or painful, or are associated with other symptoms like fever or weight loss. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent more serious conditions. Dental professionals have the necessary tools and expertise to offer tailored advice and interventions, further highlighting the importance of regular dental check-ups as part of maintaining overall Dentistry Toothtruth.
Conclusion: Proactive Oral Health Management
In summary, while most oral ulcers have the potential to heal on their own, monitoring the duration and severity of symptoms is essential to avoid unnecessary complications. By implementing effective self-care techniques and seeking professional guidance when necessary, individuals can alleviate discomfort and potentially uncover underlying health issues. For those in the U.S. and beyond, maintaining proactive oral health practices is imperative in managing and preventing oral ulcers. For more detailed guidance, consider consulting resources available at Dentistry Toothtruth.


 Rodeo Dental & Orthodontics of Phoenix4.0 (108 review)
Rodeo Dental & Orthodontics of Phoenix4.0 (108 review) Dentistry for Children of Jackson4.0 (545 review)
Dentistry for Children of Jackson4.0 (545 review) Piscataway Family Dental3.0 (518 review)
Piscataway Family Dental3.0 (518 review) River Run Dental4.0 (469 review)
River Run Dental4.0 (469 review) Blue Whale Children's Dentistry of Hawaii4.0 (21 review)
Blue Whale Children's Dentistry of Hawaii4.0 (21 review) Kelly Orthodontics5.0 (14 review)
Kelly Orthodontics5.0 (14 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile