Understanding the Risks: Can Oral Sex Transmit Diseases?
Oral sex is a common and intimate part of many relationships, but it carries health risks that many people do not fully understand. Yes, oral sex can transmit diseases, including various sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Awareness about how these infections spread and how to protect oneself is crucial to maintaining sexual health.
In the United States, rates of STIs have been rising, partly due to misconceptions about the safety of oral sex compared to other sexual activities. Understanding which diseases can be transmitted through oral contact and the factors influencing transmission can help people make safer choices and reduce health risks.
1. Types of Diseases That Can Be Transmitted Through Oral Sex
Several infections can be passed through oral sex, affecting the mouth, throat, genitals, or anus. Commonly transmitted diseases include:
Human Papillomavirus (HPV): This virus can cause genital warts and is linked to oropharyngeal cancers. HPV is one of the most common STIs transmitted through oral sex.
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 can be transmitted orally, causing cold sores or genital herpes.
Gonorrhea: Oral gonorrhea affects the throat and can cause sore throat or no symptoms at all, making it easy to unknowingly spread.
Chlamydia and Syphilis: These bacterial infections can also be passed through oral contact, sometimes causing sores or inflammation.
HIV: While less common, HIV transmission through oral sex is possible, especially if there are cuts or sores in the mouth.
2. Factors That Increase the Risk of Transmission
Not everyone engaging in oral sex will contract an infection, but several factors can elevate the risk, including:
Presence of Cuts or Sores: Open wounds or oral ulcers provide a direct entry point for pathogens.
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inflammation or gum disease can increase susceptibility to infections.
Multiple Sexual Partners: Having multiple partners raises the chance of exposure to STIs.
Unprotected Oral Sex: Lack of barrier methods such as condoms or dental dams increases risk.
3. Symptoms to Watch For After Oral Sex
Symptoms of oral STIs may be mild or mistaken for other conditions, making awareness vital. Look out for:
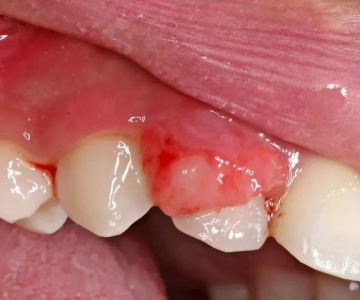
Sores or Blisters: Around the mouth, throat, or genital areas.
Sore Throat or Difficulty Swallowing: Especially if persistent and unexplained.
Unusual Discharge or Bad Breath: Could indicate infection.
Swollen Lymph Nodes: Near the neck or jaw.
If any symptoms arise, seeking prompt medical evaluation and testing is important for diagnosis and treatment.
How to Reduce the Risk: Safe Practices for Oral Sex
Prevention is the most effective way to reduce the risk of disease transmission during oral sex. Consider these practical safety tips:
Use Barrier Protection: Condoms for fellatio and dental dams for cunnilingus significantly reduce contact with bodily fluids.
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups help keep gums healthy and reduce vulnerability.
Avoid Oral Sex with Active Sores or Infections: Wait until any symptoms have healed completely.
Limit Number of Sexual Partners: Reducing exposure lowers the overall risk.
Regular STI Testing: Especially if sexually active with new or multiple partners, routine screening is critical.
Real-Life Stories Highlighting the Importance of Awareness
Jessica, a 27-year-old from Texas, discovered she had oral gonorrhea after experiencing a persistent sore throat. Initially unaware that oral sex could transmit STIs, she delayed seeking care. Once diagnosed, Jessica’s story underscored the need for better education and open communication about oral sex risks.
Another example is Mike and Lisa, a couple from New York who started using dental dams after learning about HPV transmission risks. Their proactive approach helped them maintain intimacy while minimizing health concerns, showing how knowledge can empower safer choices without sacrificing closeness.
Seeking Professional Advice and Support
If you have questions or concerns about oral sex and disease transmission, consulting healthcare professionals is crucial. They can provide personalized advice, recommend testing, and discuss preventive measures tailored to your lifestyle.
For trusted information and resources, the website Dentistry Toothtruth offers expert guidance on oral health and sexual wellness, helping individuals navigate these sensitive topics with confidence and care.



 Dr. Peter Murchie5.0 (1 review)
Dr. Peter Murchie5.0 (1 review) Contemporary Dental Implant Centre4.0 (79 review)
Contemporary Dental Implant Centre4.0 (79 review) Rainbow Dental Care4.0 (91 review)
Rainbow Dental Care4.0 (91 review) Village Pediatric Dentistry4.0 (11 review)
Village Pediatric Dentistry4.0 (11 review) Reve Orthodontics - Midtown Atlanta4.0 (258 review)
Reve Orthodontics - Midtown Atlanta4.0 (258 review) Mansolillo Jeffrey B D.M.D5.0 (459 review)
Mansolillo Jeffrey B D.M.D5.0 (459 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile