What is the Difference Between Gingivitis and Periodontitis?
Maintaining good oral health goes beyond just brushing and flossing. Understanding the conditions that affect your gums is crucial to overall dental well-being.Among the most common gum issues are gingivitis and periodontitis. While both are forms of gum disease, they represent different stages and require different treatments. In this article, we delve into the differences between gingivitis and periodontitis, providing you with the essential knowledge to recognize and manage these conditions effectively.
The Basics: Understanding Gingivitis
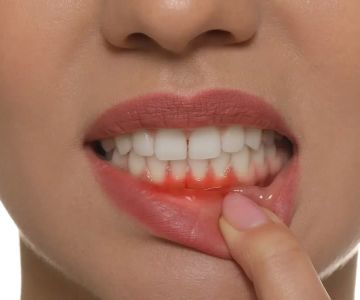
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, marked by inflammation of the gums. It is primarily caused by plaque buildup along the gumline,which can occur due to inadequate oral hygiene. The most noticeable symptoms include redness, swelling, and bleeding gums, particularly during brushingor flossing. Importantly, gingivitis does not involve any loss of bone or connective tissue, making it a reversible condition with proper care.Maintaining regular dental visits and practicing good oral hygiene habits, such as thorough brushing and flossing, can effectively manage and even reverse gingivitis. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly half of Americans suffer from some form of gum disease, highlighting the importance of addressing gingivitis early.
Progression to Periodontitis
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more serious stage of gum disease. In periodontitis, the inner layers of the gums and bonepull away from the teeth, forming pockets that can collect debris and become infected. As the disease progresses, these pockets deepen and more gum tissueand bone are destroyed, which can eventually lead to tooth loss. Periodontitis is not completely reversible, but with appropriate dental intervention and improved oral care, its progression can be hindered. Risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, and genetic predisposition can exacerbate the severity of periodontitis, making it essential to address these variables for effective management.
Key Differences in Symptoms
While gingivitis and periodontitis share some symptoms, there are key differences that can help in their identification. Gingivitis is typically characterized by painless gum irritation, while periodontitis may present with unpleasant symptoms such as chronic bad breath, gum recession, and visible pus between the teeth and gums. Additionally, tooth mobility or shifting is a hallmark of advanced periodontitis, contrasting with gingivitis where the structural integrity of the teeth remains largely intact. The American Academy of Periodontology notes that recognizing these differences can empower patients to seek timely and appropriate treatment, crucial in preventing extensive dental procedures or tooth loss.
Treatment Approaches
Treating gingivitis primarily involves a comprehensive oral hygiene regimen and routine professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar. Dentists may recommend antimicrobial mouth rinses along with regular visits to monitor gum health. In contrast, treating periodontitis requires a more aggressive approach due to the potential for serious complications. Non-surgical treatments, such as scaling and root planing, aim to cleanse the periodontal pockets. In more severe cases, surgical interventions might be necessary, including flap surgery or bone grafts. A personalized treatment plan from a dental professional is critical, as the extent of periodontitis can vary widely among individuals.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Prevention remains the most effective strategy against both gingivitis and periodontitis. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene habits, andlifestyle changes such as quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing these conditions. Maintaining a balanced diet rich invitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C and calcium, supports gum health. Dentistry Toothtruthoffers resources and expert guidance to help you stay on top of your oral health and prevent potential dental issues before they arise.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between gingivitis and periodontitis is fundamental to managing gum disease effectively. By recognizing the symptoms,causes, and treatments, individuals can take proactive measures to maintain healthy gums. Remember that early intervention can prevent the progressionof gum disease and reduce the risk of tooth loss. If you suspect any signs of gum disease, consult with dental professionals for timely diagnosis andpersonalized treatment plans. By taking preventive actions and staying informed, you can ensure lasting oral health and overall well-being.






 Smile Academy Pediatric Dentistry4.0 (48 review)
Smile Academy Pediatric Dentistry4.0 (48 review) ABC Dental4.0 (433 review)
ABC Dental4.0 (433 review) Arpino Orthodontics5.0 (133 review)
Arpino Orthodontics5.0 (133 review) Nashua Dentistry and Orthodontics for Children4.0 (370 review)
Nashua Dentistry and Orthodontics for Children4.0 (370 review) Comfort Care Dental4.0 (1156 review)
Comfort Care Dental4.0 (1156 review) Maddison Ave Dental4.0 (83 review)
Maddison Ave Dental4.0 (83 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile