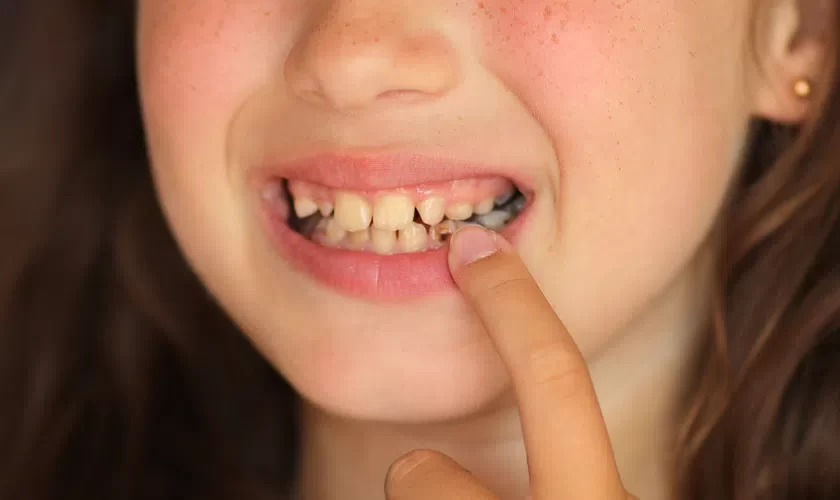
Tooth Decay and Its Relationship to Oral Cancer: Understanding the Connection
- 1. Overview: Tooth Decay and Oral Cancer
- 2. How Tooth Decay Can Contribute to Oral Cancer
- 3. Prevention Strategies: Combating Both Tooth Decay and Oral Cancer
- 4. Real-Life Examples of Tooth Decay and Oral Cancer Connection
- 5. Conclusion: Protecting Your Health through Oral Hygiene
1. Overview: Tooth Decay and Oral Cancer
Tooth decay, also known as cavities, is a widespread dental issue caused by the accumulation of plaque and bacteria that attack tooth enamel. On the other hand, oral cancer refers to cancer that develops in the tissues of the mouth, throat, and lips. While these two conditions may seem unrelated, research shows that there is a significant connection between poor oral health, particularly tooth decay, and the increased risk of oral cancer.
Individuals with severe tooth decay or untreated cavities are at a higher risk of developing oral cancer. The bacteria that cause tooth decay can lead to infections, which may damage oral tissues and increase the chances of mutations that result in cancerous growths. In this article, we will explore how tooth decay can influence oral cancer development and offer tips for prevention.
2. How Tooth Decay Can Contribute to Oral Cancer
Tooth decay and oral cancer share several common risk factors, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption. The relationship between tooth decay and oral cancer can be understood through the following mechanisms:
- Chronic Inflammation: Persistent tooth decay causes chronic inflammation in the gums and other oral tissues. Chronic inflammation is a known risk factor for cancer, as it can lead to cellular damage and increase the likelihood of cancerous mutations.
- Bacterial Infections: The bacteria responsible for tooth decay can invade the tissues of the mouth and cause infections. These infections can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off cancer cells.
- Impaired Healing: Tooth decay can hinder the body's natural ability to heal. When cavities are left untreated, the damaged tissue can become vulnerable to further infections or growth of cancer cells.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with untreated oral infections may experience a weakened immune response, which can increase the risk of cancer development, including oral cancer.
While tooth decay alone may not directly cause oral cancer, it creates an environment that is more conducive to the growth of cancer cells, making oral hygiene and regular dental care crucial for reducing the risk of both conditions.
3. Prevention Strategies: Combating Both Tooth Decay and Oral Cancer
Preventing tooth decay and oral cancer requires a combination of good oral hygiene practices, a healthy lifestyle, and regular dental checkups. Here are some essential prevention strategies:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, floss regularly, and use mouthwash to reduce bacteria buildup. This helps to prevent tooth decay and reduces the risk of infections that may contribute to oral cancer.
- Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and heavy drinking are significant risk factors for both tooth decay and oral cancer. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol consumption can greatly reduce your risk of developing these conditions.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports oral health and helps prevent tooth decay. Certain foods like berries and leafy greens contain antioxidants that may help reduce the risk of oral cancer.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. Early detection of cavities, gum disease, or oral cancer can help prevent more serious issues down the line.
- Protective Treatments: Dental sealants and fluoride treatments can help prevent tooth decay, while early screening tests for oral cancer can detect any potential issues early on.
By adopting these preventive measures, you can maintain optimal oral health and reduce the risk of both tooth decay and oral cancer.
4. Real-Life Examples of Tooth Decay and Oral Cancer Connection
Let's take the case of John, a 50-year-old man who had struggled with poor oral hygiene for many years. He frequently consumed sugary foods and drinks, and his teeth showed signs of severe decay. After years of neglect, John began to notice persistent pain in his mouth, along with swelling and bleeding from his gums.
When John visited his dentist, he was diagnosed with advanced tooth decay and referred to an oncologist for further examination. Sadly, the dentist discovered early signs of oral cancer. John's case highlights the importance of addressing tooth decay early and maintaining good oral hygiene to prevent serious complications, including oral cancer.
Another example is that of Sarah, a non-smoker who always kept up with regular dental visits. She was diligent about her oral hygiene and avoided alcohol. By staying proactive about her dental health, Sarah avoided both tooth decay and the risks associated with oral cancer. Her case underscores the effectiveness of preventive care in reducing the chances of developing serious health issues.
5. Conclusion: Protecting Your Health through Oral Hygiene
In conclusion, while tooth decay and oral cancer are distinct conditions, they share a significant connection. The bacteria and infections associated with untreated tooth decay can increase the risk of developing oral cancer. By maintaining excellent oral hygiene, avoiding harmful lifestyle habits, and scheduling regular dental checkups, you can protect yourself from both tooth decay and oral cancer.
If you're concerned about tooth decay or oral cancer risk, visit Dentistry Toothtruth for more information and professional advice on oral health care and prevention.






 ADVANCED SMILES PC4.0 (205 review)
ADVANCED SMILES PC4.0 (205 review) Cal Dental of Van Nuys4.0 (109 review)
Cal Dental of Van Nuys4.0 (109 review) Dr. Dhaval Shah, DDS1.0 (1 review)
Dr. Dhaval Shah, DDS1.0 (1 review) Dentistry for Children - Cumming Midway4.0 (275 review)
Dentistry for Children - Cumming Midway4.0 (275 review) Dr. James C. Kincaid5.0 (39 review)
Dr. James C. Kincaid5.0 (39 review) Smile Dental of New Rochelle5.0 (242 review)
Smile Dental of New Rochelle5.0 (242 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile