- Understanding Tooth Abscess
- Causes of Tooth Abscesses
- How Antibiotics Help Treat a Tooth Abscess
- Steps for Treating a Tooth Abscess with Antibiotics
- When to Seek Professional Care for a Tooth Abscess
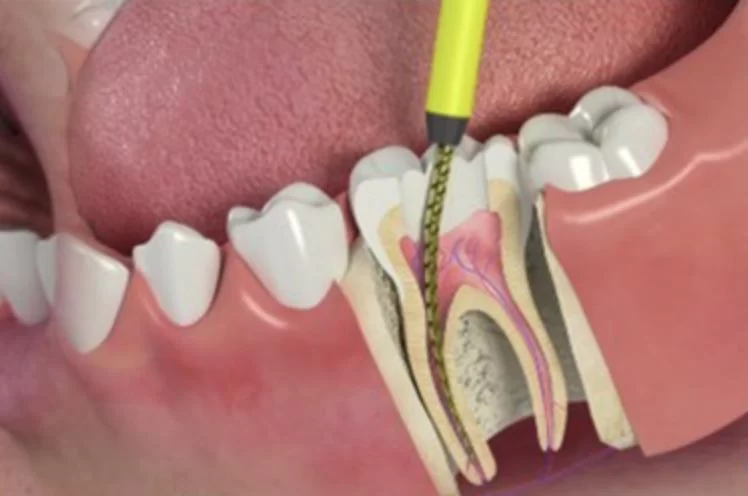
Understanding Tooth Abscess
A tooth abscess is a painful, pus-filled infection that can develop within the tooth or the surrounding gum tissue. It is typically caused by bacterial infection and can occur when a tooth becomes decayed or damaged, allowing bacteria to enter the tooth’s pulp. The infection may spread to the surrounding tissues, resulting in a visible swelling or bump on the gums, along with throbbing pain. Left untreated, an abscess can lead to serious complications, including the spread of the infection to other parts of the body.
Causes of Tooth Abscesses
Tooth abscesses are commonly caused by poor dental hygiene, which allows plaque and bacteria to build up and attack the teeth and gums. Other potential causes include:
- Cavities: When cavities are left untreated, bacteria can invade the inner parts of the tooth and lead to an abscess.
- Gum Disease: Periodontal diseases can weaken the gums, making them more susceptible to infections.
- Trauma to the Tooth: A cracked or broken tooth can expose the inner pulp to bacteria, resulting in an infection.
- Previous Dental Procedures: In some cases, complications from previous dental work, like a filling or root canal, can cause an abscess if bacteria were introduced.
How Antibiotics Help Treat a Tooth Abscess
Antibiotics are often the first line of treatment for a tooth abscess, as they help control the infection and prevent it from spreading. These medications work by killing the bacteria that are causing the infection, reducing inflammation, and alleviating pain. Typically, a dentist will prescribe antibiotics before performing a dental procedure to drain the abscess, allowing the tooth to heal effectively. Common antibiotics prescribed for a tooth abscess include:
- Amoxicillin: A common antibiotic used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including tooth abscesses.
- Clindamycin: Often prescribed for patients who are allergic to penicillin or for more severe infections.
- Metronidazole: Sometimes used in conjunction with other antibiotics to treat more complex abscesses or infections in the mouth.
While antibiotics can help to manage the infection, they are not a cure for the abscess itself. In most cases, the abscess will need to be drained by a dentist to fully treat the condition.
Steps for Treating a Tooth Abscess with Antibiotics
If you are prescribed antibiotics to treat a tooth abscess, it’s important to follow the treatment plan carefully to ensure the infection is properly managed. Here are the general steps for treating a tooth abscess with antibiotics:
- Consult a Dentist: A dentist will assess the severity of the abscess and determine whether antibiotics are appropriate. They may also suggest additional treatments, such as drainage or a root canal, depending on the situation.
- Start the Antibiotic Course: Take the prescribed antibiotics exactly as directed. Even if the symptoms improve, continue the full course to ensure the infection is completely eradicated.
- Monitor Symptoms: While on antibiotics, monitor any changes in your symptoms. If the swelling decreases and the pain subsides, this is a good sign. However, if the symptoms worsen, contact your dentist immediately.
- Follow Up with a Dental Procedure: After the infection is under control, your dentist may recommend further treatment, such as draining the abscess or performing a root canal to remove the source of the infection.
When to Seek Professional Care for a Tooth Abscess
While antibiotics can provide temporary relief and help control a tooth abscess, professional care is crucial to fully treat the condition. You should seek immediate dental care if:
- The pain becomes severe: If the pain from the abscess becomes unbearable or constant, it’s time to consult a dentist.
- The swelling spreads: If the swelling around the abscess spreads to other areas of the face or neck, it could indicate the infection is spreading, which requires urgent attention.
- Fever develops: A fever can indicate that the infection is severe and spreading beyond the tooth. Seek medical help immediately.
- The abscess doesn’t improve: If your symptoms don’t improve after completing the antibiotic course, or if they get worse, a follow-up visit with your dentist is essential.
At Dentistry Toothtruth, we offer a wide range of dental care products and services that can help prevent and manage tooth abscesses. If you experience a tooth abscess, don't wait for the problem to escalate. Visit us to learn about the best treatment options available for your dental health.







 Kathleen Thieu, DDS, MS4.0 (16 review)
Kathleen Thieu, DDS, MS4.0 (16 review) EZ Dental Specialty Group3.0 (20 review)
EZ Dental Specialty Group3.0 (20 review) Tender Smiles 4 Kids4.0 (450 review)
Tender Smiles 4 Kids4.0 (450 review) Summit Dental Specialists5.0 (13 review)
Summit Dental Specialists5.0 (13 review) Dracut Dental Group5.0 (268 review)
Dracut Dental Group5.0 (268 review) Nashua Cosmetic & Restorative Dentistry, PLLC4.0 (51 review)
Nashua Cosmetic & Restorative Dentistry, PLLC4.0 (51 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile