Soft Tissue Grafting: The Ultimate Guide to Gum Graft Surgery and Oral Tissue Repair
- What Is Soft Tissue Grafting?
- Why Is Soft Tissue Grafting Needed?
- Types of Soft Tissue Grafts
- The Soft Tissue Grafting Procedure
- Recovery and Aftercare
- Where to Get Soft Tissue Grafting
1. What Is Soft Tissue Grafting?
Soft tissue grafting, also known as gum graft surgery, is a dental procedure that helps restore lost gum tissue caused by gum recession, periodontal disease, or trauma. This treatment involves taking healthy tissue from another part of the mouth and grafting it onto the affected area to enhance both function and aesthetics.
By reinforcing the gumline, soft tissue grafting prevents further recession, reduces tooth sensitivity, and enhances overall oral health. It is commonly performed by periodontists and oral surgeons specializing in advanced gum treatments.
2. Why Is Soft Tissue Grafting Needed?
Gum recession is a common issue that can lead to severe dental problems if left untreated. Some of the main reasons why soft tissue grafting is necessary include:
- Preventing Tooth Sensitivity: Exposed tooth roots due to gum recession can lead to pain and discomfort, especially when consuming hot or cold foods.
- Protecting Tooth Roots: When gums recede, the root surfaces become vulnerable to decay, wear, and infection.
- Enhancing Smile Aesthetics: Receding gums can make teeth appear longer, impacting the overall appearance of a smile.
- Preventing Further Gum and Bone Loss: Severe gum recession can contribute to tooth loss and compromise jawbone integrity.
- Supporting Dental Restorations: For patients with dental implants or crowns, sufficient gum tissue is essential for long-term stability.
If left untreated, gum recession can lead to significant oral health issues, making soft tissue grafting a valuable solution.
3. Types of Soft Tissue Grafts
There are different types of soft tissue grafts, depending on the patient’s needs and the severity of gum recession. The most common types include:
- Connective Tissue Graft: This is the most common technique, where tissue is taken from beneath the surface of the patient’s palate and grafted onto the affected gum area.
- Free Gingival Graft: This method involves taking tissue directly from the roof of the mouth and attaching it to the area needing coverage. It is often used for patients with thin gums.
- Pedicle Graft: Instead of taking tissue from another area, this technique uses nearby gum tissue to cover the recession, preserving blood supply and promoting faster healing.
- Allograft or Donor Tissue Graft: In some cases, tissue from a donor source or synthetic materials may be used to enhance gum volume.
Your periodontist will determine the best grafting method based on your specific needs and oral health condition.
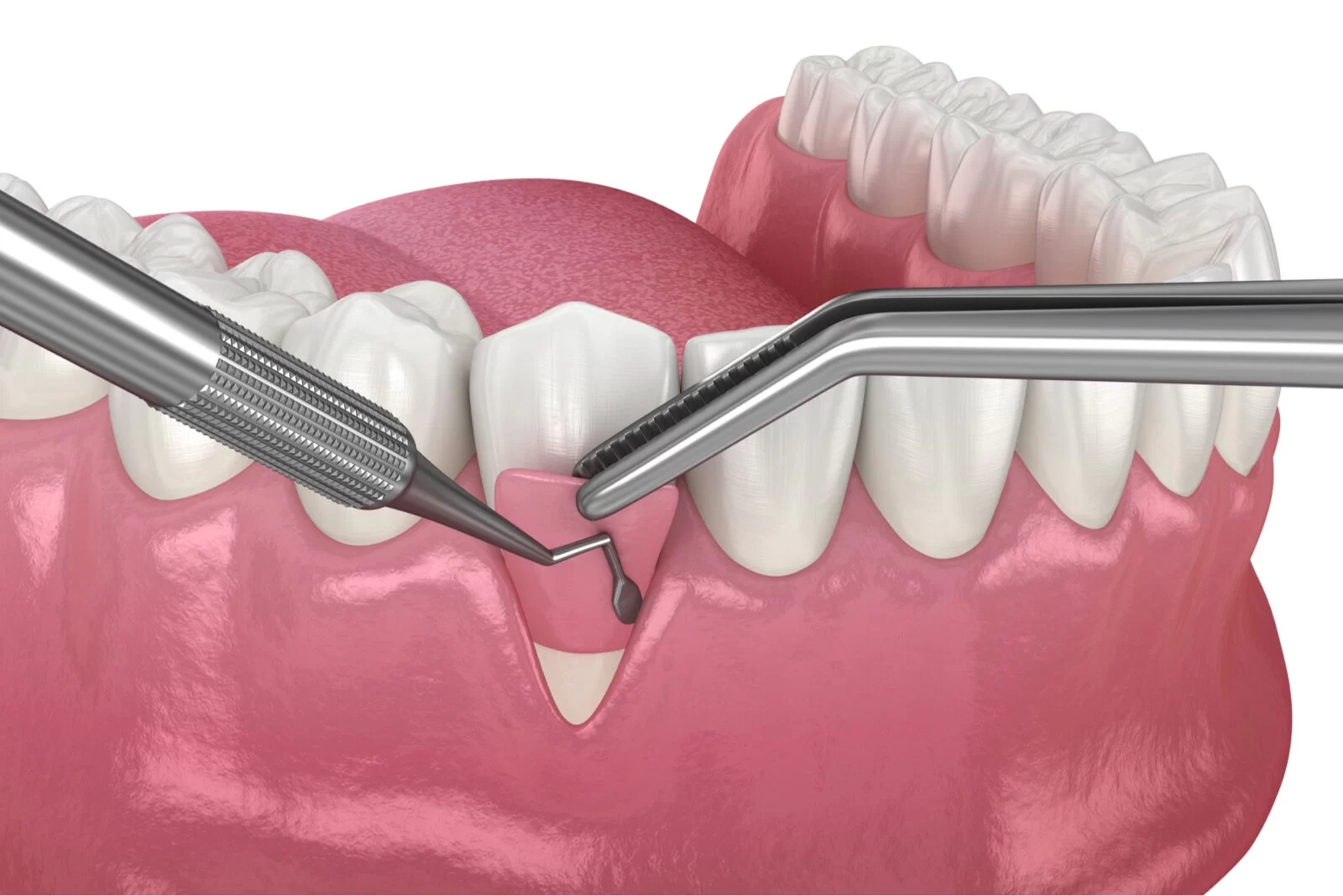
4. The Soft Tissue Grafting Procedure
Understanding the steps involved in soft tissue grafting can help ease any concerns about the procedure. Here’s what to expect:
- Initial Consultation: Your dentist or periodontist will evaluate your gum health and discuss the best grafting technique.
- Local Anesthesia: The treatment area is numbed to ensure a painless procedure.
- Tissue Harvesting: If autografting (using the patient’s own tissue), the donor site is prepared and tissue is removed.
- Grafting Process: The harvested tissue is placed over the receding gum area and secured with sutures.
- Healing and Monitoring: A protective dressing may be placed, and follow-up visits will be scheduled to ensure proper healing.
The entire process usually takes about an hour, and most patients experience minimal discomfort during and after the procedure.
5. Recovery and Aftercare
Proper aftercare is essential to ensure a smooth healing process. Here are key tips for recovery:
- Follow Dietary Restrictions: Stick to soft foods like yogurt, soup, and mashed potatoes for the first few days.
- Avoid Brushing the Treated Area: Your dentist will provide guidelines on when and how to resume brushing near the graft site.
- Use Prescribed Medications: Pain relievers and antibiotics may be recommended to prevent infection and discomfort.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: These can slow healing and increase the risk of complications.
- Attend Follow-Up Appointments: Regular checkups ensure that the graft is integrating properly and healing as expected.
Following these aftercare tips will help maximize the success of your soft tissue grafting procedure.
6. Where to Get Soft Tissue Grafting
If you’re experiencing gum recession or need soft tissue grafting, choosing a qualified periodontist is crucial for successful treatment. Here are some recommended providers:
- Dentistry Toothtruth: A trusted provider in periodontal care, Dentistry Toothtruth offers advanced soft tissue grafting solutions. Schedule a consultation here.
- Periodontal Specialists: Seek experienced periodontists who specialize in gum grafting and advanced oral tissue repair.
- Cosmetic and Restorative Dentistry Clinics: Many dental clinics provide integrated smile restoration treatments, including soft tissue grafting.
- University Dental Schools: Some dental schools offer affordable grafting procedures performed by supervised professionals.
By choosing an experienced provider, you can ensure a safe and effective soft tissue grafting procedure that restores your gums and enhances your smile.







 Bismarck Dentistry4.0 (44 review)
Bismarck Dentistry4.0 (44 review) Highland Dental Clinic: Dr. Robert Klein5.0 (7 review)
Highland Dental Clinic: Dr. Robert Klein5.0 (7 review) Baystate Family Dental4.0 (27 review)
Baystate Family Dental4.0 (27 review) Bright Now! Dental & Orthodontics4.0 (221 review)
Bright Now! Dental & Orthodontics4.0 (221 review) Georgetown Family Dentistry4.0 (359 review)
Georgetown Family Dentistry4.0 (359 review) Westlake Family Dentistry4.0 (155 review)
Westlake Family Dentistry4.0 (155 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile