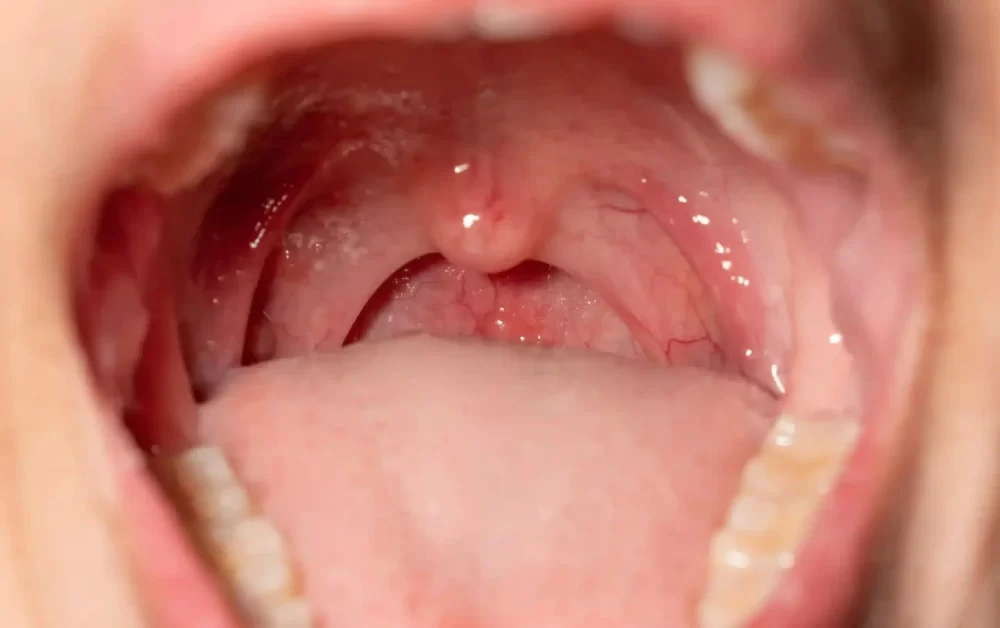
Signs That Your Tooth Pain Is Related to an Infection – Recognizing and Treating Dental Infections
- 1. Understanding Tooth Infections
- 2. Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
- 3. How to Know If Your Tooth Pain Is from Infection
- 4. Treatment Options for Tooth Infections
- 5. Preventing Tooth Infections
If you’ve been dealing with tooth pain, it can be difficult to pinpoint whether the pain is caused by a simple cavity or something more serious like a tooth infection. I’ve been there myself—wondering if that persistent throbbing in my tooth is just a minor issue or something that requires immediate attention. Recognizing the signs that your tooth pain is related to an infection is crucial, as untreated dental infections can lead to more severe health complications. In this article, we’ll explore how to identify the symptoms of a tooth infection, how to differentiate it from other types of dental pain, and what treatment options are available to address it.
1. Understanding Tooth Infections
Tooth infections occur when bacteria enter the inner part of your tooth, known as the pulp. This area contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue. If the pulp becomes infected, it can lead to abscesses, severe pain, and even damage to the surrounding bones and tissues. The most common cause of tooth infection is tooth decay, but it can also occur due to gum disease, cracked teeth, or other dental injuries.
In my own experience, I didn’t realize how quickly a small cavity could develop into a serious infection until I started feeling a constant, sharp pain in my tooth. If left untreated, the infection can spread to other areas of your mouth and even affect your overall health, so it’s important to catch it early and take the necessary steps to prevent it from worsening.
2. Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of a tooth infection can help you determine whether your tooth pain is related to an infection. Some common signs of a dental infection include:
2.1. Intense Throbbing Pain
One of the hallmark symptoms of a tooth infection is severe, throbbing pain that doesn’t go away. It may come in waves and feel more intense when you lie down or chew. I remember feeling a sharp, pulsating pain that seemed to radiate through my jaw and even into my ear at times. This is often a sign that the infection is deep within the tooth pulp.
2.2. Sensitivity to Temperature
If your tooth pain worsens when exposed to hot or cold temperatures, it could be a sign of an infection. The nerves in the pulp become inflamed, making the tooth sensitive to temperature changes. This sensitivity may last longer than typical tooth sensitivity and can make drinking or eating uncomfortable.
2.3. Swelling and Redness
Another clear sign of a tooth infection is swelling around the affected tooth or gumline. If the infection has spread to the surrounding tissues, you may notice swelling, redness, or tenderness in your gums. I experienced swelling near my gumline, which was one of the signs that alerted me to the fact that I might have an infection.
2.4. Abscess or Pus Buildup
A visible abscess, or pocket of pus, near the affected tooth is another symptom of a tooth infection. This is typically accompanied by a foul taste or smell in the mouth. If you notice any drainage from your gums, it’s important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the infection from spreading.
2.5. Fever and Malaise
If the infection is severe, it can cause general symptoms of illness, such as fever, fatigue, or a general feeling of being unwell. I remember feeling feverish and exhausted when my infection progressed to a more serious stage. These symptoms can indicate that the infection has spread to the surrounding tissues or even into your bloodstream.
3. How to Know If Your Tooth Pain Is from Infection
It can be difficult to differentiate between a simple toothache and a tooth infection. Here are some key differences that can help you identify if your tooth pain is due to an infection:
3.1. Duration and Intensity of Pain
If your tooth pain has been persistent for more than a day or two and has become progressively worse, there’s a high chance that the pain is related to an infection. A regular toothache due to a cavity or other issue typically subsides after a few hours or with over-the-counter pain relief.
3.2. Sensitivity to Pressure
If your tooth hurts when you apply pressure to it, such as when biting down or chewing, it could indicate an infection. A typical cavity might cause discomfort when eating sweet, cold, or hot foods, but if pressure increases the pain, an infection is more likely.
3.3. Visible Changes in Your Tooth or Gums
Look for any visible signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, or pus around the affected tooth. If you notice any of these symptoms, you should consult a dentist immediately to avoid complications.
4. Treatment Options for Tooth Infections
If you suspect that your tooth pain is caused by an infection, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible. The dentist will diagnose the infection and recommend the appropriate treatment. Common treatments for tooth infections include:
4.1. Antibiotics
In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed to treat the infection and reduce swelling. Antibiotics can help stop the spread of the infection and prevent it from worsening while other treatments are being planned.
4.2. Root Canal Therapy
If the infection is confined to the pulp of the tooth, a root canal may be necessary to remove the infected tissue. This treatment helps save the tooth and alleviate the pain associated with the infection.
4.3. Tooth Extraction
If the infection has caused significant damage to the tooth, extraction may be required to prevent the spread of the infection to other parts of your mouth. While this is often a last resort, it may be necessary in severe cases.
5. Preventing Tooth Infections
Preventing tooth infections begins with good oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting your dentist for regular checkups can help you avoid many common dental problems, including infections. Here are a few additional tips to keep your teeth healthy:
5.1. Use Fluoride Toothpaste
Fluoride helps to strengthen enamel and protect your teeth from decay. I personally find that using fluoride toothpaste has helped me maintain strong teeth and prevent infections from forming.
5.2. Avoid Sugary Foods and Drinks
Sugary foods and drinks promote tooth decay, which can lead to infections. Limiting your intake of sugary snacks and drinks will help protect your teeth and reduce the risk of infection.
If you’re experiencing tooth pain and suspect it may be due to an infection, don’t wait to seek professional help. Visit Dentistry Toothtruth to learn more about preventing and treating dental infections. Early intervention is key to avoiding long-term dental problems and ensuring your smile stays healthy and beautiful.







 Kanwar Gill, BDS0.0 (0 review)
Kanwar Gill, BDS0.0 (0 review) Light Dental Studios of 6th Ave5.0 (19 review)
Light Dental Studios of 6th Ave5.0 (19 review) Art & Science Family Dentistry5.0 (202 review)
Art & Science Family Dentistry5.0 (202 review) Family & Spa Dentistry4.0 (178 review)
Family & Spa Dentistry4.0 (178 review) Kalil Dental Group4.0 (44 review)
Kalil Dental Group4.0 (44 review) Ocean Dental4.0 (141 review)
Ocean Dental4.0 (141 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile