- 1 - Understanding Oral Infections—what-they-are-and-why-they-matter
- 2 - Common Signs and Symptoms—how-to-recognize-an-oral-bacterial-infection
- 3 - Real Case Example—a-patient-story-on-gum-swelling-and-pain
- 4 - Treatment Options Available—professional-and-home-care-choices
- 5 - Expert Insights—dentist-perspectives-on-infections
- 6 - Prevention Strategies—daily-habits-that-reduce-bacterial-risks
- 7 - Family Dentistry Online—resources-and-guidance-for-dental-care
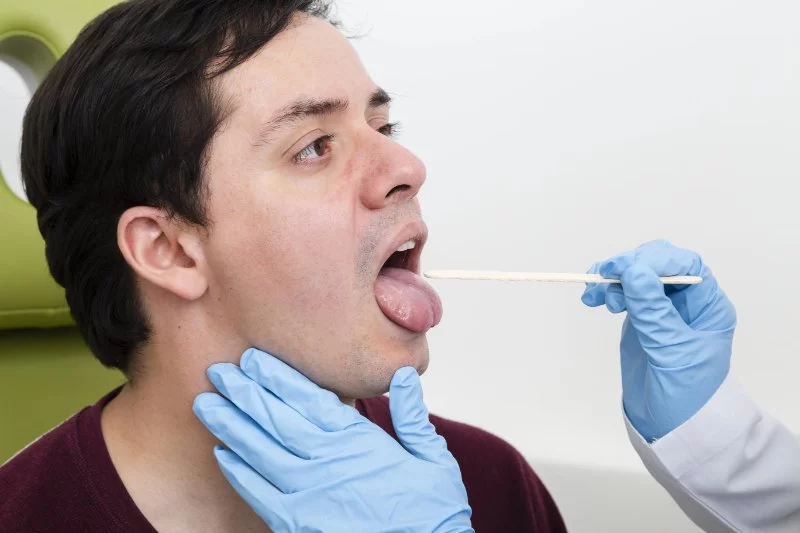
1. Understanding Oral Infections
Signs of oral bacterial infection and treatment options available are essential topics for anyone who values dental health. Oral infections occur when harmful bacteria multiply in the mouth, often as a result of poor hygiene, untreated cavities, or weakened immune defenses. These infections can range from minor gum irritation to serious abscesses that spread beyond the mouth if left untreated. Recognizing them early ensures faster recovery and prevents long-term damage.
1.1 Why Oral Health Matters
Infections in the mouth are not just local issues—they can affect overall health. Studies have linked oral bacteria to heart disease, diabetes complications, and systemic inflammation, making early detection and treatment vital.
2. Common Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the early signs helps prevent escalation. Typical symptoms of oral bacterial infections include persistent bad breath, swollen or bleeding gums, tooth pain, pus around teeth or gums, sensitivity when chewing, and in some cases, fever. Each symptom can vary in intensity but should never be ignored.
2.1 Gum and Tooth Indicators
Swollen gums, especially if red and tender, often signal gingivitis or early periodontitis. A sharp or throbbing toothache accompanied by swelling may indicate a dental abscess. Both conditions require prompt dental attention.
3. Real Case Example
A young professional in Chicago ignored mild gum bleeding for months, assuming it was from brushing too hard. Over time, her gums swelled, and she developed persistent tooth pain. A dentist diagnosed her with a bacterial gum infection and early abscess. After professional cleaning, antibiotics, and improved hygiene, her symptoms resolved. This case highlights how small symptoms can lead to severe infections if untreated.
4. Treatment Options Available
Treatment depends on the severity and type of infection. Mild cases may be managed with professional cleanings, antibacterial rinses, and improved oral care routines. Moderate infections often require antibiotics, while severe cases such as abscesses may need drainage or root canal therapy. In extreme situations, tooth extraction could be necessary to stop the spread of bacteria.
4.1 At-Home Relief
While professional care is essential, home remedies can provide short-term relief. Saltwater rinses, cold compresses, and over-the-counter pain relievers help ease discomfort until dental care is available.
5. Expert Insights
Dentists emphasize that untreated infections can progress rapidly. According to dental professionals, patients often wait too long to seek help, which complicates treatment and recovery. Experts recommend scheduling check-ups every six months and immediately contacting a dentist at the first sign of infection.
6. Prevention Strategies
Preventing bacterial infections is more effective than treating them. Brushing twice a day, flossing daily, limiting sugar intake, and attending regular dental visits reduce risk significantly. Additionally, quitting smoking and maintaining a balanced diet support gum health and immunity against bacteria.
7. Family Dentistry Online
If you want to learn more about signs of oral bacterial infection and treatment options available, Family Dentistry Online 【 】 provides reliable resources, professional advice, and recommended products. Whether you need guidance on daily care, insight into treatment options, or trusted services, Family Dentistry Online 【 】 is your go-to partner for oral health support.







 Lourdes's Dentistry - Affordable Dentist4.0 (160 review)
Lourdes's Dentistry - Affordable Dentist4.0 (160 review) Silc Periodontics4.0 (169 review)
Silc Periodontics4.0 (169 review) Doc Bresler's Cavity Busters4.0 (363 review)
Doc Bresler's Cavity Busters4.0 (363 review) McCall Family Dentistry5.0 (718 review)
McCall Family Dentistry5.0 (718 review) Justin Ewell, DMD at Suncoast Dental Goodyear0.0 (0 review)
Justin Ewell, DMD at Suncoast Dental Goodyear0.0 (0 review) Harbor Point Dental at Pelham Manor4.0 (118 review)
Harbor Point Dental at Pelham Manor4.0 (118 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile