How Can You Tell if an Oral Ulcer is Caused by an Infection or Another Issue?
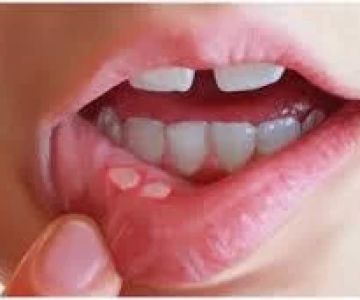
Oral ulcers, commonly known as canker sores, are painful, open sores that develop on the inside of the mouth. While often benign and self-limiting, they can be a source of significant discomfort, affecting speech and eating. Distinguishing the underlying cause of an oral ulcer is crucial for effective treatment. Infection is a common culprit, but many other factors can contribute to the development of ulcers. Understanding whether an infection or another issue is at play is essential for appropriate care and treatment.
Identifying Symptoms of Infectious Oral Ulcers
When an oral ulcer emerges due to an infection, particular symptoms and characteristics can help in its identification. Infectious ulcers are often accompanied by systemic symptoms such as fever and malaise. A bacterial infection, for example, may lead to pus formation and an unpleasant odor, signaling the presence of purulent material. Likewise, viral infections, such as those caused by the herpes simplex virus, often present with clusters of painful vesicles that rupture and form ulcers. These types of ulcers are usually preceded or accompanied by a tingling or burning sensation in the afflicted area.
Determining whether an infection is the cause can involve observing the ulcer’s physical characteristics. Infectious ulcers tend to be more persistent and may not easily resolve without medical intervention. For instance, ulcers stemming from a fungal infection like oral thrush generally appear as white lesions and require antifungal treatment. Consulting with a healthcare professional and possibly conducting laboratory tests such as cultures might be necessary to confirm the infectious nature of the ulcer.
In summary, paying attention to systemic symptoms and the features of the ulcer itself can provide clues that point to an infectious origin. It is always recommended to seek medical advice when dealing with ulcers that appear resistant to regular over-the-counter treatments or if accompanied by systemic symptoms.
Non-Infectious Causes of Oral Ulcers
Not all oral ulcers are caused by infections. A variety of non-infectious factors, including trauma, nutritional deficiencies, and autoimmune disorders, can also lead to ulcers. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis, also known as canker sores, is one of the most common types of non-infectious oral ulcers. Unlike ulcers caused by infections, these sores are not contagious and typically have a well-demarcated edge with a white or yellow center.
Trauma-induced ulcers might result from biting the cheek, dental work irritations, or aggressive brushing. These ulcers generally improve when the source of irritation is removed. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly of vitamin B12, iron, and folate, have been linked to mouth ulcers, suggesting that a comprehensive dietary assessment could be beneficial if ulcers are present without obvious cause.
Additionally, autoimmune conditions like Behçet's disease or systemic lupus erythematosus can manifest with oral ulcers. In such cases, ulcers may accompany other systemic signs that reflect a more systemic origin. Diagnosis of non-infectious ulcers typically involves a thorough review of medical history and possibly laboratory investigations.
Diagnostic Approaches for Oral Ulcers
Diagnosing the cause of oral ulcers begins with a detailed medical and dental history review and a thorough oral examination. Understanding the patient's dietary habits, recent illnesses, stress levels, and any history of recurring ulcers provides essential context. Physicians and dentists often use a multifaceted approach to diagnose the cause of oral ulcers, which may include blood tests to check for nutritional deficiencies, an immune system profile, or culture tests if an infection is suspected.
Doctors might also employ imaging techniques like an oral lesion biopsy, especially if malignancy needs ruling out. Dermoscopy, a non-invasive skin imaging technique, can be helpful in examining suspicious lesions more closely. Collaboration between dental professionals and medical specialists can significantly aid in determining the underlying cause of ulcers, ensuring that patients receive a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to their specific condition.
Treatment and Management of Oral Ulcers
The treatment plan for oral ulcers largely depends on the underlying cause, so accurate diagnosis is pivotal. For infectious ulcers, addressing the source is key, which might involve antibiotics for bacterial infections, antivirals for viral infections, or antifungal agents for fungal infections. Supportive care, such as maintaining good oral hygiene, using antiseptic mouthwashes, and avoiding spicy or acidic foods, aids in symptom relief.
Non-infectious ulcers often require symptom management, primarily through topical treatments like corticosteroid ointments or gels to reduce inflammation and pain. It's also crucial to correct any underlying nutritional deficiencies through supplements or dietary adjustments. In cases of underlying autoimmune conditions, systemic medication may be necessary.
A holistic approach, including stress management techniques such as mindfulness or relaxation exercises, can be highly beneficial since stress is a common exacerbating factor for non-infectious ulcers. Regular dental check-ups can help in the early detection and management of potential ulcer-causing factors like sharp teeth or ill-fitting dentures.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, differentiating between infectious and non-infectious causes of oral ulcers is essential for timely and effective treatment. Recognizing the indicative symptoms, engaging in comprehensive diagnostic evaluations, and collaborating with healthcare professionals can provide clarity in treatment. For American readers, maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking prompt dental or medical advice when ulcers present atypical characteristics are vital steps for preserving oral health.
To be proactive about dental care, it’s important to stay informed and prepared. Utilize resources like Dentistry Toothtruth for up-to-date information and guidance on oral health issues. Implementing regular oral health checkups and adhering to professional recommendations can significantly reduce the impact of oral ulcers and improve overall well-being.


 Dr. Marvin R. Winter, DDS5.0 (9 review)
Dr. Marvin R. Winter, DDS5.0 (9 review) Oral Surgery Services Inc4.0 (89 review)
Oral Surgery Services Inc4.0 (89 review) Woodbury Dental Associates4.0 (231 review)
Woodbury Dental Associates4.0 (231 review) A Tooth Fairy Dental4.0 (463 review)
A Tooth Fairy Dental4.0 (463 review) Hawthorne Dental Associates5.0 (463 review)
Hawthorne Dental Associates5.0 (463 review) Parkway Dental Associates0.0 (0 review)
Parkway Dental Associates0.0 (0 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile