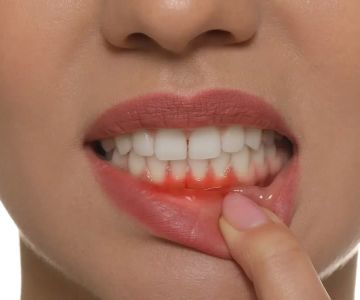
Understanding Gum Recession
Gum recession is a prevalent dental problem that occurs when the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, exposing the roots. This can be caused by a multitude of factors such as aggressive brushing, smoking, periodontal disease, genetic predisposition, and even trauma to the gum tissue. Gum recession not only makes the teeth more vulnerable to cavities and sensitivity but can also lead to more serious oral health issues if left untreated.
Symptoms and Causes of Gum Recession
The most obvious symptom of gum recession is the exposure of the tooth roots. Other warning signs include pain or discomfort near the gum line, sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet substances, and increased sensitivity during brushing and flossing. The causes of gum recession are diverse. Brushing too hard or with an incorrect technique can damage the gums and enamel. The buildup of dental plaque and tartar can also contribute to gum disease and subsequent recession. Periodontal disease, a bacterial infection that affects the gums and supporting bone, is a major cause. Additionally, factors like smoking, having a lip or tongue piercing, and abnormal tooth positioning can increase the risk of gum recession.
Diagnosis and Tests for Gum Recession
Your dentist can diagnose gum recession during a routine examination by measuring the amount of gum recession on each tooth using a special instrument called a periodontal probe. They will also assess the depth of the periodontal pockets around the teeth. Healthy pockets typically measure between 1 and 3 millimeters. Larger pockets indicate gum disease and a higher risk of gum recession.
Management and Treatment Options
Unfortunately, receding gums cannot grow back completely. However, there are measures to prevent the condition from worsening and manage the associated symptoms. For sensitivity caused by gum recession, dentists can apply fluoride varnish or other desensitizing agents. Desensitizing toothpaste can also be used at home. When it comes to treating gum recession, the approach depends on the severity and cause. Mild cases may benefit from nonsurgical treatments such as topical antibiotics, dental bonding, or orthodontics. In more severe cases, gum recession surgery is often necessary. Gum graft surgery is a common and effective procedure where gum tissue is transplanted to cover the exposed roots. The recovery time after gum grafting surgery varies depending on several factors, but most patients feel back to normal within two weeks.
Prevention of Gum Recession
While gum recession cannot always be prevented, especially if there is a genetic predisposition, you can significantly reduce the risk by maintaining proper oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth thoroughly twice a day, flossing daily, using an antimicrobial mouthwash twice a day, following your dentist's recommendations for teeth cleanings, using a soft-bristled toothbrush, and avoiding smoking and chewing tobacco. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for early detection and intervention.
Outlook and Prognosis
If gum recession is detected early and treated appropriately, the chances of managing the condition and preventing further damage are good. However, if left untreated, gum recession can progress and lead to serious complications such as bone loss, tooth mobility, and tooth loss. It's important to seek dental advice promptly if you notice any signs of gum recession.
Living with Gum Recession
If you suspect you have gum recession, it's essential to see your healthcare provider promptly. Asking the right questions during your dental visit can help you understand your condition better and make informed decisions about treatment. Questions such as the severity of the gum recession, available nonsurgical options, the recommended type of gum grafting surgery if necessary, the chances of recurrence, and the frequency of teeth cleanings can provide valuable insights.
Natural Approaches to Reverse Gum Recession
There are several natural remedies that may help in reversing gum recession or at least reducing its severity. Using essential oils like eucalyptus, peppermint, and tea tree oil can have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. Drinking green tea, consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and using saltwater rinses can also contribute to gum health. Aloe vera gel, septilin, and turmeric may have beneficial properties in treating gum recession. However, it's important to note that these natural approaches should complement professional dental care and not replace it.
In conclusion, gum recession is a common dental concern that requires attention and appropriate management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, and by practicing good oral hygiene and seeking timely dental care, you can take significant steps towards maintaining healthy gums and teeth.






 Happy Smile Dental4.0 (44 review)
Happy Smile Dental4.0 (44 review)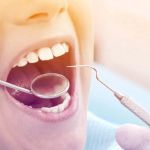 Cary Dental Rejuvenation4.0 (473 review)
Cary Dental Rejuvenation4.0 (473 review) Orthodontic Associates of Collegeville, PC Adam J. Weiss DMD & Sarah S. Pavlow DMD5.0 (46 review)
Orthodontic Associates of Collegeville, PC Adam J. Weiss DMD & Sarah S. Pavlow DMD5.0 (46 review) Family Dental Care4.0 (212 review)
Family Dental Care4.0 (212 review) Dr. Joyce Dentistry4.0 (204 review)
Dr. Joyce Dentistry4.0 (204 review) Periodontics & Implant Center of Manasquan4.0 (311 review)
Periodontics & Implant Center of Manasquan4.0 (311 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile