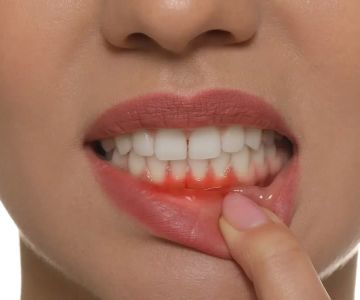
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease refers to the inflammation and infection of the tissues that support your teeth. It can start due to poor oral hygiene, but some individuals may be genetically predisposed to it. Poor hygiene leads to the buildup of dental plaque, which contains harmful bacteria that can cause gum problems. The progression of gum disease can result in gum recession, tooth loss, and other complications.
Symptoms and Stages of Gum Disease
Symptoms of gum disease may include red or purplish gums, bleeding, soreness, bad breath, unpleasant taste, pain when chewing, gum recession, loose teeth, and changes in the way your teeth fit together. There are four stages of gum disease: gingivitis (the earliest stage), mild periodontitis, moderate periodontitis, and advanced periodontitis. Early detection and treatment are crucial as the disease progresses gradually and may not cause pain initially.
Risk Factors and Complications
Several factors increase the risk of developing gum disease, such as smoking, poor oral hygiene, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, hormonal changes, stress, genetics, and heart disease. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and has been linked to other health problems like heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Diagnosis and Tests
Dentists can diagnose gum disease during a routine examination by looking for plaque buildup and asking about your symptoms. They may use a periodontal probe to measure the pockets around your teeth and take dental X-rays to assess bone loss. A referral to a periodontist might be necessary for a more detailed evaluation and treatment plan.
Management and Treatment Options
Although gum disease is not curable, it is manageable with appropriate treatment. For early-stage gum disease (gingivitis), routine dental cleaning and improved oral hygiene can reverse the condition. Other treatments include scaling and root planing for mild gum disease, pocket reduction surgery for moderate to advanced gum disease, bone grafts to replace lost bone, gum grafts to restore gum tissue, guided tissue regeneration, and the use of platelet-rich fibrin or plasma for enhanced healing.
Prevention and Outlook
Most cases of gum disease can be prevented with consistent and proper oral hygiene, including brushing teeth two to three times a day, flossing daily, using antibacterial mouthwash, avoiding smoking, and visiting the dentist for regular cleanings and exams. The outlook for gum disease is manageable with early detection and treatment, but it can lead to other health conditions if the infection spreads.
When to See a Dentist and Common Questions
If you experience bleeding, tender, or swollen gums, it's essential to see a dentist promptly. If diagnosed with gum disease, it's advisable to ask your periodontist questions such as the stage of the disease, the required treatment type (surgical or nonsurgical), sedation options, recovery time, when you can return to work or school, and the frequency of dental cleanings.
Gum disease is a serious oral health concern that requires attention and proper care. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and available treatments, you can take proactive steps to maintain good oral hygiene and seek timely medical intervention if needed. Early detection and appropriate management are key to preserving your teeth and overall health.





 Allan Neal A DDS5.0 (17 review)
Allan Neal A DDS5.0 (17 review) Downer Place Dental & Orthodontics4.0 (634 review)
Downer Place Dental & Orthodontics4.0 (634 review) High Point Dental Group4.0 (510 review)
High Point Dental Group4.0 (510 review) Udis & Sethi Orthodontics5.0 (128 review)
Udis & Sethi Orthodontics5.0 (128 review) Madison Oral Surgery & Dental Implants4.0 (661 review)
Madison Oral Surgery & Dental Implants4.0 (661 review) Dental Arts of Totowa4.0 (80 review)
Dental Arts of Totowa4.0 (80 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile