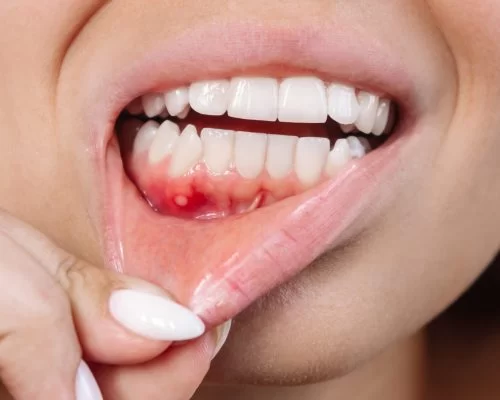
Gum Disease Management: How to Prevent and Treat Gum Disease Effectively
- 1. Understanding Gum Disease
- 2. Common Symptoms of Gum Disease
- 3. Effective Ways to Prevent Gum Disease
- 4. Treating Gum Disease: From Mild to Severe
- 5. The Role of Your Dentist in Gum Disease Management
- 6. Recommended Products for Managing Gum Disease
1. Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It typically begins with the accumulation of plaque on the teeth, which, if not removed, can lead to inflammation and infection of the gums. There are two primary stages of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the milder form and can often be reversed with good oral hygiene, while periodontitis is more severe and may result in tooth loss if not treated.
The causes of gum disease include poor oral hygiene, smoking, certain medical conditions like diabetes, and genetic factors. Managing gum disease requires a comprehensive approach, focusing on prevention, early detection, and proper treatment.
2. Common Symptoms of Gum Disease
Recognizing the symptoms of gum disease early is crucial to preventing its progression. Some common symptoms include:
1. Bleeding Gums
One of the first signs of gum disease is gums that bleed when brushing or flossing. If your gums bleed regularly, it's important to consult with your dentist.
2. Swollen and Red Gums
Healthy gums should be firm and pale pink. Swollen, red, or tender gums are often a sign of gingivitis or more advanced gum disease.
3. Bad Breath
Persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be a result of bacterial build-up caused by gum disease. If you notice an unpleasant odor despite brushing, it's time to take action.
4. Loose Teeth
In more advanced stages of periodontitis, the supporting bone structures of the teeth can be destroyed, leading to loose teeth. This is a clear sign of a severe gum disease case that requires immediate attention.
3. Effective Ways to Prevent Gum Disease
Prevention is the key to managing gum disease effectively. Here are some essential steps to keep your gums healthy:
1. Brush and Floss Regularly
Brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste is essential for removing plaque and preventing the buildup that leads to gum disease. Flossing at least once a day helps clean between the teeth, areas that your toothbrush can’t reach.
2. Use Antibacterial Mouthwash
Using an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce plaque and prevent gum disease by killing harmful bacteria in the mouth. This is especially important for people with a history of gum issues.
3. Quit Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease as it weakens the immune system and makes it harder for the gums to heal. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk of gum disease.
4. Eat a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in vitamins, especially Vitamin C, helps maintain healthy gums. Avoid excessive sugar, as it can lead to plaque buildup and increase the risk of gum disease.
4. Treating Gum Disease: From Mild to Severe
The treatment for gum disease depends on its severity. Here’s a breakdown of treatments based on the stage of the disease:
1. Gingivitis Treatment
For gingivitis, the condition can often be reversed with proper brushing, flossing, and professional cleaning. Your dentist will remove the plaque and tartar buildup, and you will be advised to improve your oral hygiene routine.
2. Periodontitis Treatment
If the disease has advanced to periodontitis, more intensive treatments are required. This can include scaling and root planing (a deep cleaning treatment) to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline. In some cases, surgical treatments may be needed to repair the damage.
3. Surgery for Advanced Cases
In severe cases where the bone supporting the teeth has been lost, surgical treatments such as gum grafts or bone grafts may be required to restore the gum tissue and bone structure.
5. The Role of Your Dentist in Gum Disease Management
While good at-home oral care is vital, your dentist plays a crucial role in managing and preventing gum disease. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings help catch early signs of gum disease and prevent it from progressing. Your dentist may recommend additional treatments such as deep cleanings or scaling to ensure your gums stay healthy.
Dental professionals also provide personalized advice on how to care for your gums based on your specific needs, including lifestyle factors like smoking or diet.
6. Recommended Products for Managing Gum Disease
There are several products available to help manage gum disease and improve gum health:
1. Sonicare Toothbrush
The Sonicare toothbrush is highly recommended for effective plaque removal and gum health. It’s designed to remove plaque more efficiently than a regular toothbrush, making it an excellent choice for those with gum disease.
2. Paroex Antiseptic Mouthwash
Paroex is an antibacterial mouthwash that helps reduce the bacteria in your mouth and prevent gum disease. It’s particularly effective for people with gingivitis or early gum disease.
3. GUM Soft-Picks
These soft, flexible picks are ideal for cleaning between teeth and along the gumline. They are a great alternative for people who find traditional flossing difficult, helping to reduce plaque buildup and maintain gum health.
If you want to learn more about gum disease management and explore products designed to support your oral health, visit [Dentistry Toothtruth](https://familydentistryonline.net).







 Hawthorn Woods Family Dental Care5.0 (535 review)
Hawthorn Woods Family Dental Care5.0 (535 review) Tend East Nashville4.0 (319 review)
Tend East Nashville4.0 (319 review) NE Philly Dentistry4.0 (7 review)
NE Philly Dentistry4.0 (7 review) Fleetwood Dental4.0 (205 review)
Fleetwood Dental4.0 (205 review) Huynh Long T DMD5.0 (7 review)
Huynh Long T DMD5.0 (7 review) Cherry Valley Dental4.0 (115 review)
Cherry Valley Dental4.0 (115 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile