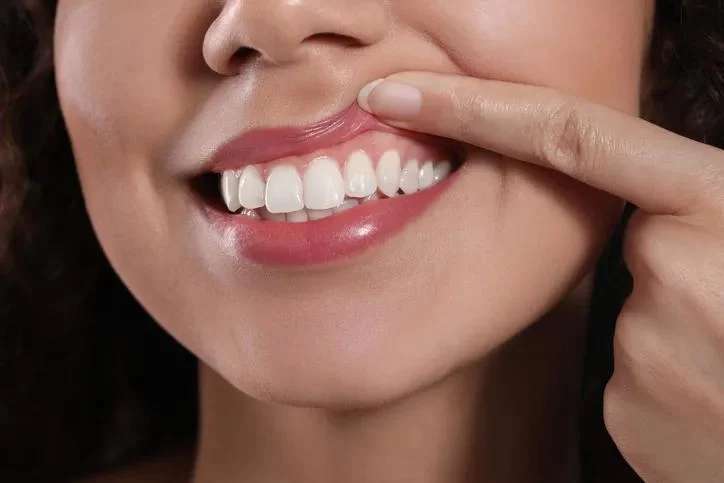

Effective Gum Disease Management for Healthier Gums and Teeth
- 1. Understanding Gum Disease
- 2. Common Symptoms of Gum Disease
- 3. How to Prevent Gum Disease
- 4. Effective Gum Disease Treatment Options
- 5. The Role of Oral Hygiene in Gum Care
- 6. When to See a Dentist for Gum Disease
1. Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease is a common yet serious condition that affects the gums and can lead to tooth loss if not managed properly. The two most common stages of gum disease are gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the early stage and can be reversed with proper care, while periodontitis is more severe and can cause lasting damage to the gums and bone structure.
Gum disease begins when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up on the teeth and gums. If plaque is not removed, it can harden into tartar, leading to inflammation of the gums. This inflammation, known as gingivitis, can progress to periodontitis if left untreated, causing the gums to recede and form pockets that become infected.
2. Common Symptoms of Gum Disease
Recognizing the symptoms of gum disease early is crucial for effective management. Common signs of gum disease include swollen or red gums, bleeding while brushing or flossing, bad breath, loose teeth, and gum recession. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek treatment to prevent the condition from worsening.
In more advanced stages, periodontitis may cause severe discomfort, tooth mobility, and changes in your bite. If these signs are left untreated, they can lead to tooth loss and more serious complications.
3. How to Prevent Gum Disease
Prevention is always better than treatment, and when it comes to gum disease, maintaining good oral hygiene is the key. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help remove plaque and prevent gum disease from developing.
Additionally, a healthy diet plays a role in gum disease prevention. Eating foods rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C, can help keep your gums healthy. Avoiding smoking is another crucial step, as tobacco products significantly increase the risk of gum disease.
4. Effective Gum Disease Treatment Options
If gum disease has already developed, there are several treatment options available, depending on the severity of the condition. For gingivitis, professional cleaning by a dentist or hygienist is often sufficient to remove plaque and tartar. If you have periodontitis, your dentist may recommend a more extensive treatment, such as scaling and root planing, to clean the deeper layers of the gums and teeth.
In some cases, surgical treatments such as gum grafts or flap surgery may be necessary to restore the gums and reduce pocketing. Antibacterial treatments, including medicated mouthwashes and antibiotics, can also help control infection and promote healing.
5. The Role of Oral Hygiene in Gum Care
Oral hygiene is the foundation of gum disease management. Proper brushing and flossing are essential to remove plaque, which can harden into tartar and lead to gum disease. Brushing at least twice a day for two minutes, using a soft-bristled toothbrush, and flossing between teeth daily help prevent the buildup of plaque and reduce the risk of gum infection.
Regular dental cleanings and checkups are also a critical part of maintaining gum health. Your dentist can spot early signs of gum disease and provide treatment before the condition becomes more severe. If you have existing gum issues, your dentist may recommend more frequent visits to manage the disease effectively.
6. When to See a Dentist for Gum Disease
If you experience any symptoms of gum disease, such as bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or tooth mobility, it’s important to seek professional dental care right away. Early intervention can prevent the condition from progressing to more severe stages, which may require more invasive treatments.
Even if you do not have noticeable symptoms, regular dental checkups every six months are essential for monitoring your gum health. Your dentist can detect early signs of gum disease and offer guidance on improving your oral hygiene routine to prevent it.
Managing gum disease requires a combination of good oral hygiene, a healthy lifestyle, and professional dental care. If you're looking to learn more about gum disease management or discover effective treatments, visit Dentistry Toothtruth for expert advice and products designed to support your gum health.







 Amana Dental3.0 (34 review)
Amana Dental3.0 (34 review) Olivia Turner Dental0.0 (0 review)
Olivia Turner Dental0.0 (0 review) Dr Stein Dental Group4.0 (226 review)
Dr Stein Dental Group4.0 (226 review) Anderson Dental Professionals5.0 (253 review)
Anderson Dental Professionals5.0 (253 review) Sage Dental of Acworth4.0 (20 review)
Sage Dental of Acworth4.0 (20 review) Fresh Smiles4.0 (132 review)
Fresh Smiles4.0 (132 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile