Fungal mouth infections, most commonly known as oral thrush or candidiasis, represent a significant yet often misunderstood oral health challenge affecting millions of Americans annually. These persistent and potentially uncomfortable conditions occur when naturally occurring Candida yeast overgrows in the mouth, disrupting the delicate balance of oral microorganisms.
Understanding Fungal Mouth Infections: The Basics
Oral fungal infections primarily develop when the body's immune system becomes compromised, allowing Candida albicans to multiply beyond normal levels. While these infections can affect individuals of all ages, certain populations—including infants, elderly patients, and those with weakened immune systems—face higher risks of developing persistent and severe symptoms.
Recognizing Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Identifying a fungal mouth infection early is crucial for effective treatment. Typical symptoms include:
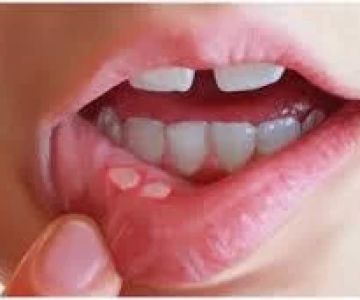
- White or yellowish patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and throat
- Painful or burning sensations in the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing
- Slight bleeding when patches are scraped
- Altered taste perception
Primary Risk Factors and Underlying Causes
Multiple factors contribute to fungal mouth infection development. Key risk factors include:
- Prolonged antibiotic usage
- Diabetes
- Chemotherapy treatments
- HIV/AIDS
- Corticosteroid medications
- Poor oral hygiene
Diagnostic Approaches and Medical Evaluation
Healthcare professionals typically diagnose fungal mouth infections through comprehensive oral examinations and, in some cases, laboratory testing. A qualified dental professional will carefully inspect the oral cavity, potentially collecting tissue samples to confirm the presence of Candida organisms.
Comprehensive Treatment Strategies
Treatment approaches vary depending on infection severity and patient health conditions. Standard interventions include:
- Antifungal medications
- Oral rinses
- Dietary modifications
- Probiotics
- Improved oral hygiene practices
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Effective prevention requires a multifaceted approach. Recommendations include maintaining excellent oral hygiene, managing underlying health conditions, and adopting lifestyle practices that support immune system functionality.
Conclusion: Taking Proactive Steps
Fungal mouth infections, while potentially challenging, are manageable with proper medical guidance and personal commitment. By understanding symptoms, recognizing risk factors, and seeking timely professional intervention, individuals can successfully navigate these oral health complexities.
Patients experiencing persistent symptoms should consult healthcare professionals promptly. Early detection and comprehensive treatment remain the most effective strategies in managing fungal mouth infections.


 Family Dental Group5.0 (2 review)
Family Dental Group5.0 (2 review) Prairie Point Dental4.0 (141 review)
Prairie Point Dental4.0 (141 review) Larchmont Orthodontics PC5.0 (8 review)
Larchmont Orthodontics PC5.0 (8 review) Tigard Modern Dentistry4.0 (169 review)
Tigard Modern Dentistry4.0 (169 review) Plum Grove Dental Center5.0 (290 review)
Plum Grove Dental Center5.0 (290 review) Sherman Oaks Dental5.0 (64 review)
Sherman Oaks Dental5.0 (64 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile