Understanding Fungal Mouth Infections
Fungal mouth infections, such as thrush or oral candidiasis, can affect people of all ages. These infections occur when there is an overgrowth of the Candida fungus in the mouth. The fungus is typically present in small amounts, but certain factors like medications, underlying health conditions, or a weakened immune system can cause it to multiply and cause problems.
Symptoms of Fungal Mouth Infections
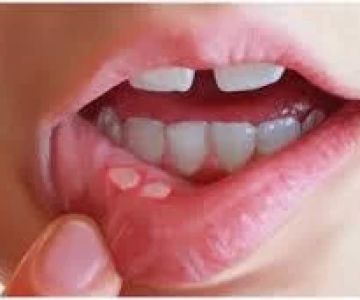
Common symptoms include creamy white, slightly raised lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, or other areas of the mouth. These lesions may cause soreness, redness, a loss of taste, a cottony feeling, and in severe cases, difficulty swallowing and pain. In individuals with compromised immune systems, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, causing more serious complications.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors increase the risk of developing fungal mouth infections. These include diabetes, anemia, HIV/AIDS, cancer, dry mouth, pregnancy, smoking, ill-fitting dentures, and the use of certain medications like corticosteroids, antibiotics, and birth control pills.
Diagnosis of Fungal Mouth Infections
A healthcare provider can usually diagnose thrush by visually inspecting the mouth for the characteristic white lesions. A microscopic examination of tissue from a lesion or additional tests such as a throat culture, endoscopy, or X-rays may be performed if the infection is suspected to have spread to the esophagus.
Treatment Options
The typical treatment for fungal mouth infections involves the use of antifungal medications. These can come in various forms such as tablets, lozenges, or liquids that are swished around in the mouth before swallowing. The duration of treatment depends on the individual's age and the cause of the infection. For those with healthy immune systems, the response to treatment is usually positive within one to two weeks. However, in individuals with weakened immune systems, symptoms may be more severe and treatment may be more challenging.
Prevention Tips
To lower the risk of fungal mouth infections, it's essential to maintain good oral hygiene. This includes brushing teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, avoiding certain mouth products, seeing a dentist regularly, limiting foods that encourage Candida growth, and quitting smoking if applicable.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice signs or symptoms of thrush, such as soreness, bleeding, or raised white areas inside the mouth, it's advisable to schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider. If symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment, or if you have a weakened immune system and experience recurrent infections, prompt medical attention is crucial.
Home Remedies and Additional Considerations
While antifungal medication is essential for clearing the infection, some home remedies may help alleviate symptoms. These include swishing with warm saltwater, taking probiotics, and consuming yogurt containing healthy bacteria. However, it's important to note that these remedies alone may not be sufficient to completely cure the infection.
In conclusion, fungal mouth infections can be uncomfortable and disruptive, but with proper diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures, they can be effectively managed. If you suspect you have a fungal mouth infection or experience persistent symptoms, consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and appropriate treatment.

 Michael Alan Pilar, DDS0.0 (0 review)
Michael Alan Pilar, DDS0.0 (0 review) Craig Q Adams, DMD5.0 (55 review)
Craig Q Adams, DMD5.0 (55 review) Western Iowa Endodontics3.0 (16 review)
Western Iowa Endodontics3.0 (16 review) COMPREHENSIVE DENTISTRY PC4.0 (18 review)
COMPREHENSIVE DENTISTRY PC4.0 (18 review) Designer Dental Services4.0 (136 review)
Designer Dental Services4.0 (136 review) Toothology5.0 (136 review)
Toothology5.0 (136 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile