Understanding Barium Sulfate Oral Check and Its Purpose
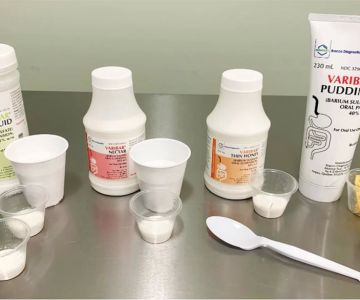
Barium sulfate oral checks, commonly known as barium swallows, are diagnostic procedures used primarily to visualize the upper gastrointestinal tract. Patients ingest a barium sulfate suspension, a radiopaque contrast agent that outlines the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum on X-ray images, allowing physicians to detect abnormalities such as strictures, ulcers, or tumors.
1. What Happens During a Barium Sulfate Oral Check?
During the procedure, the patient drinks a chalky liquid containing barium sulfate. This substance coats the lining of the digestive tract, making it visible on X-ray scans. The process is painless and usually completed within a few minutes, providing critical information for accurate diagnosis.
2. The Role of Barium Sulfate as a Contrast Agent
Barium sulfate is inert and not absorbed by the body; it passes through the digestive system and is eliminated naturally in stool. Its unique property of blocking X-rays helps create clear images without exposing patients to radiation beyond the imaging itself.
Does Barium Sulfate Oral Check Affect Kidney Function?
A common concern among patients undergoing barium swallow tests is whether the barium sulfate used can impact kidney health, especially those with pre-existing kidney conditions.
1. How Barium Sulfate Is Processed by the Body
Since barium sulfate is not absorbed into the bloodstream but remains within the gastrointestinal tract, it does not enter the kidneys or circulate through the blood. Therefore, it generally poses no risk to kidney function, unlike some other contrast agents such as iodinated contrasts used in CT scans.
2. Comparing Barium Sulfate to Other Contrast Agents
Contrast agents used in imaging vary in their potential effects on kidneys. Iodine-based contrasts can sometimes cause contrast-induced nephropathy, especially in patients with compromised kidney function. Barium sulfate’s safety profile is different because it does not interact with the kidneys, making it a preferred option for gastrointestinal imaging in patients with kidney concerns.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions of Barium Sulfate Oral Check
While barium sulfate oral checks are generally safe, some patients may experience minor side effects or require special precautions.
1. Common Side Effects
Patients might notice temporary constipation or changes in stool color due to the barium passing through the digestive system. Drinking plenty of fluids post-procedure is often recommended to help clear the barium from the body efficiently.
2. Rare Complications and When to Seek Medical Help
In rare cases, patients with bowel obstructions or perforations may face complications if barium sulfate leaks into the abdominal cavity. Although unrelated to kidney function, such situations require immediate medical attention. Discussing your full medical history with your healthcare provider before the procedure helps minimize risks.
Real Patient Experiences and Expert Insights
Maria, a 60-year-old patient with chronic kidney disease, shared her concerns before a barium swallow test. “I was worried about my kidneys, but my doctor explained that barium sulfate doesn’t affect kidney function since it doesn’t enter the bloodstream. This reassurance helped me go through the procedure without anxiety.”
Dr. Steven, a radiologist, explains, “Barium sulfate is safe for patients with kidney issues because it remains within the digestive tract. However, we always review patient history carefully to ensure the test is appropriate.”
When to Consult a Specialist and How to Prepare
If you have kidney problems or other health concerns, discussing them with your healthcare provider before scheduling a barium sulfate oral check is essential. They might recommend additional precautions or alternative diagnostic methods if needed.
1. Pre-Test Consultation and Disclosure
Inform your medical team about any kidney disease, allergies, or medications you are taking. This transparency ensures personalized care and safety during imaging procedures.
2. Post-Test Care Recommendations
After the procedure, drinking plenty of fluids helps flush out the barium from your system and reduces constipation risk. Report any unusual symptoms like severe abdominal pain or difficulty passing stool to your healthcare provider immediately.
For reliable advice, expert diagnostics, and trusted imaging services, Dentistry Toothtruth offers resources to connect you with healthcare providers experienced in safe radiologic procedures.




 Gardena Dental Care4.0 (416 review)
Gardena Dental Care4.0 (416 review) Sunflower Dental Group4.0 (37 review)
Sunflower Dental Group4.0 (37 review) Designer Dental Services4.0 (136 review)
Designer Dental Services4.0 (136 review) Glamorous Smile Dental Spa5.0 (17 review)
Glamorous Smile Dental Spa5.0 (17 review) Ivy Dental of Fleetwood4.0 (9 review)
Ivy Dental of Fleetwood4.0 (9 review) Ichimura Dave DDS0.0 (0 review)
Ichimura Dave DDS0.0 (0 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile