Understanding the Risks: Can You Get Diseases from Oral Sex?
Oral sex is a common sexual activity, but many people wonder if it carries the risk of transmitting diseases. The answer is yes—oral sex can indeed spread several sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Understanding which infections can be transmitted, how to protect yourself, and what symptoms to watch for is crucial to maintaining good sexual health.
Common STIs Transmitted Through Oral Sex
1. Oral Herpes (HSV-1 and HSV-2)
Oral herpes is caused mainly by the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), but HSV-2 (more common in genital herpes) can also be transmitted orally. This infection is highly contagious and can be spread through oral-genital contact even when no visible sores are present. Symptoms include painful cold sores or blisters around the mouth, but many people carry the virus without showing symptoms.
2. Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is another infection that can infect the throat after oral sex with an infected partner. Often, throat gonorrhea shows no symptoms but can cause sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or swollen lymph nodes. If untreated, it can lead to serious complications. Testing and treatment are straightforward, but many are unaware that gonorrhea can affect the throat.
3. Syphilis
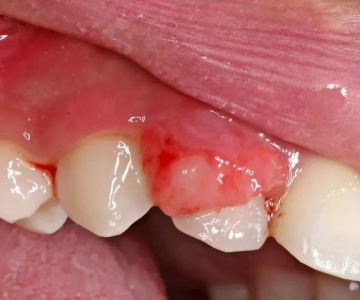
Syphilis can cause sores (chancres) in the mouth or throat after oral sex with an infected individual. These sores might be painless and unnoticed but are highly infectious. If left untreated, syphilis progresses through several stages and can cause severe long-term health problems.
4. Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV is a common virus with many strains, some of which can cause warts in the oral region or increase the risk of oral cancers. Oral HPV is usually asymptomatic and hard to detect without medical testing, but it can be transmitted through oral sex.
5. Chlamydia
Though less common than genital chlamydia, this infection can also affect the throat through oral sex. Symptoms are often mild or absent, but the infection can spread and cause complications if untreated.
Real-Life Scenario: The Story of Jake and Emma
Jake and Emma, a young couple living in California, thought oral sex was risk-free until Jake developed a persistent sore throat and swollen glands. After visiting a healthcare provider, he was diagnosed with oral gonorrhea, a surprise to both. They had always practiced safe sex with condoms but did not use protection during oral sex. This experience led them to learn about the risks of oral STIs and to adopt safer oral sex practices.
How to Protect Yourself During Oral Sex
1. Use Barriers
Dental dams and condoms provide effective protection against many oral STIs. Using these barriers consistently during oral sex significantly reduces transmission risks.
2. Regular STI Testing
Regular screening is essential, even if you have no symptoms. Many oral infections can be asymptomatic but still contagious. Testing helps with early detection and treatment.
3. Avoid Oral Sex During Outbreaks
If you or your partner have visible sores or symptoms of an infection like herpes, avoid oral sex until fully healed to prevent spreading the infection.
4. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Healthy gums and mouth tissues can reduce susceptibility to infections. Brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are part of overall sexual health.
Symptoms to Watch for After Oral Sex
Although many oral STIs can be asymptomatic, some signs that warrant medical attention include:
- Sores, blisters, or ulcers in or around the mouth
- Sore throat lasting more than a few days
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Unexplained mouth pain or difficulty swallowing
- White patches or unusual discoloration in the mouth
The Importance of Open Communication
Talking honestly with your partner(s) about sexual health, STI history, and testing is vital. These conversations build trust and help reduce risks for both parties. Remember, oral sex is part of sexual intimacy and should be approached with the same care and respect as other sexual activities.
Accessing Reliable Sexual Health Resources
In the United States, many clinics and healthcare providers offer confidential testing and treatment for oral STIs. The more you know, the better you can protect yourself. For personalized advice, treatment options, and prevention strategies, consult professionals who specialize in sexual health.
For the best recommendations and services related to oral and dental health intertwined with sexual health, visit Dentistry Toothtruth, where expert guidance is available to help you maintain both oral hygiene and overall wellbeing.



 James B Ford DDS4.0 (87 review)
James B Ford DDS4.0 (87 review) Blessed Smile Dentistry of Yorba Linda4.0 (42 review)
Blessed Smile Dentistry of Yorba Linda4.0 (42 review) Northwood Dental4.0 (471 review)
Northwood Dental4.0 (471 review) Jonathan Threadgill, DMD5.0 (5 review)
Jonathan Threadgill, DMD5.0 (5 review) Angela Manning DDS PC4.0 (66 review)
Angela Manning DDS PC4.0 (66 review) David G. Jones, DDS - TMJ Treatment Atlanta3.0 (2 review)
David G. Jones, DDS - TMJ Treatment Atlanta3.0 (2 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile