Understanding Gum Disease and Its Impact on Oral Health
Gum disease, medically known as periodontal disease, is a common but serious infection that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It begins with plaque buildup, which if left untreated, causes inflammation, gum recession, and ultimately tooth loss. Beyond dental issues, gum disease can influence overall oral health and contribute to other complications.
One question frequently asked by patients in the United States is whether gum disease can cause oral thrush, a fungal infection of the mouth. Exploring this relationship helps us understand how interconnected oral conditions can affect each other.
What Is Oral Thrush and How Does It Develop?
Oral thrush is caused by an overgrowth of Candida, a type of yeast naturally found in the mouth. Under normal conditions, the balance between microorganisms keeps Candida in check. However, when this balance is disrupted—due to weakened immunity, antibiotic use, or oral infections like gum disease—Candida can multiply excessively, leading to white patches, soreness, and discomfort.
Oral thrush affects many people, particularly those with compromised immune systems, diabetes, or poor oral hygiene. It’s essential to recognize early signs and seek treatment promptly to prevent worsening symptoms.
Exploring the Connection: Can Gum Disease Cause Oral Thrush?
While gum disease itself is primarily bacterial, its presence can create an environment that encourages fungal infections like oral thrush. Inflamed and damaged gum tissue can compromise the mouth’s natural defenses, making it easier for Candida to thrive.
Moreover, treatments for gum disease sometimes involve antibiotics, which can unintentionally disrupt the microbial balance in the mouth, increasing the risk of oral thrush. This indirect link shows how managing gum disease effectively is crucial to preventing secondary infections.
Therefore, gum disease doesn't directly cause oral thrush, but it can significantly contribute to the conditions that allow oral thrush to develop.
Recognizing Symptoms of Both Gum Disease and Oral Thrush
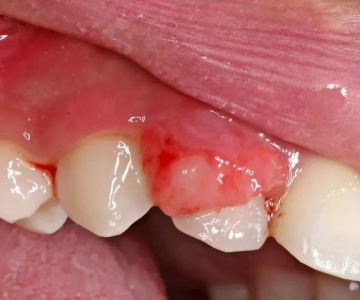
Gum disease symptoms include red, swollen, or bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, and gum recession. Oral thrush typically presents as creamy white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, or roof of the mouth, accompanied by soreness and difficulty swallowing.
Understanding these symptoms is vital for early diagnosis. If you notice overlapping signs, consulting a dental professional promptly can prevent complications and improve treatment outcomes.
Real-Life Story: How Addressing Gum Disease Helped Resolve Oral Thrush
Maria, a 58-year-old woman, struggled with persistent oral thrush despite antifungal treatments. Upon dental examination, her dentist discovered advanced gum disease was creating a conducive environment for the fungal infection. Once Maria began comprehensive gum therapy, including professional cleaning and improved oral hygiene, her oral thrush symptoms diminished significantly.
This case illustrates how treating underlying gum issues can effectively control secondary infections like oral thrush and restore oral health.
Preventive Measures and Treatment Options
Prevention remains the best strategy. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups are essential to control plaque and prevent gum disease. Avoiding excessive antibiotic use and maintaining a balanced diet also help keep oral flora healthy.
If oral thrush develops, antifungal medications are typically prescribed. Simultaneously managing gum health supports recovery and reduces recurrence risks. Professional dental care combined with home oral hygiene forms the foundation of effective treatment.
Maintaining Long-Term Oral Health
Keeping both gum disease and oral thrush at bay requires consistent care and awareness. People prone to infections should inform their dentists about their medical history to tailor preventive strategies effectively.
For those seeking expert advice and comprehensive dental care, Dentistry Toothtruth offers personalized services and recommendations to support your journey toward optimal oral health.



 Lil Smile Builders Children's Dentistry4.0 (566 review)
Lil Smile Builders Children's Dentistry4.0 (566 review) Rapid City Dental Clinic4.0 (90 review)
Rapid City Dental Clinic4.0 (90 review) Spencer Dental & Braces4.0 (459 review)
Spencer Dental & Braces4.0 (459 review) BGW Dental Group4.0 (292 review)
BGW Dental Group4.0 (292 review) Smile Garden at Midlothian Children's Dentistry4.0 (603 review)
Smile Garden at Midlothian Children's Dentistry4.0 (603 review) Dr. Beth A. O'Connor, DDS4.0 (96 review)
Dr. Beth A. O'Connor, DDS4.0 (96 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile