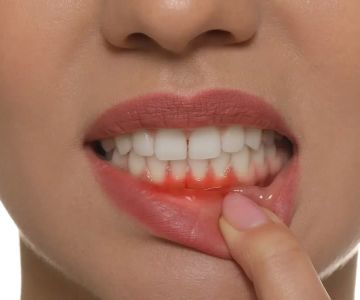
What Causes Gum Recession?
Gum recession occurs for several reasons. Periodontal diseases, which are bacterial gum infections, can destroy the gum tissue and the supporting bone that hold your teeth in place. This is the main cause of gum recession. Some people may be genetically predisposed to gum diseases, making them more susceptible regardless of their oral care routine. Aggressive brushing, insufficient dental hygiene, hormonal fluctuations in women, tobacco use, teeth grinding, crooked or misaligned teeth, and body jewelry rubbing against the gums can all contribute to gum recession.
Treatment Options for Gum Recession
Mild cases of gum recession might be improved with nonsurgical treatments such as topical antibiotics to eliminate harmful bacteria, dental bonding to camouflage the exposed area, or orthodontics to correct misaligned teeth. In more severe cases, gum graft surgery is often necessary. During this procedure, a gum graft is taken from the roof of the mouth or sometimes from sterilized human donor tissue and is stitched into place to replace the missing gum tissue. The recovery time after gum grafting surgery varies depending on several factors, but most people feel back to normal within about two weeks.
Prevention of Gum Recession
Although gum recession can't always be prevented, especially if you have a genetic predisposition to thin gum tissue, you can significantly reduce the risk by practicing proper teeth and gum care. This includes brushing your teeth thoroughly twice a day, flossing once a day, using an antimicrobial mouthwash twice daily, following your dentist's recommendation for teeth cleanings, using a soft-bristled toothbrush, and avoiding smoking and chewing tobacco. Regular visits to the dentist for check-ups are crucial, especially if you notice any signs of gum recession.
Conclusion
Gum recession is a significant oral health concern that can have various causes and require different treatment approaches. While it can't be reversed completely, timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment can prevent it from worsening and protect your teeth and overall oral health. By maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking professional advice promptly when needed, you can minimize the impact of gum recession and enjoy a healthy smile for a long time.






 Palm Valley Orthodontics5.0 (3 review)
Palm Valley Orthodontics5.0 (3 review) Valley View Dental4.0 (1195 review)
Valley View Dental4.0 (1195 review) Kellyn Hodges Orthodontics4.0 (301 review)
Kellyn Hodges Orthodontics4.0 (301 review) Dr. Joshua A. Bresler, DMD3.0 (5 review)
Dr. Joshua A. Bresler, DMD3.0 (5 review) Niver & Sobel5.0 (4 review)
Niver & Sobel5.0 (4 review) Leila Zamiri DDS - Cherry Office4.0 (134 review)
Leila Zamiri DDS - Cherry Office4.0 (134 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile