What Are Oral Diseases? Understanding Common Oral Health Issues
Oral diseases are conditions that affect the mouth, teeth, gums, and surrounding structures. They can range from minor issues like cavities to serious diseases that impact your overall health. While many oral diseases are preventable with good hygiene practices, some can develop unnoticed until they cause significant pain or discomfort. This article will explore the most common oral diseases, their causes, symptoms, and how they can be treated or prevented.
1. What Causes Oral Diseases?
Oral diseases are primarily caused by bacteria and plaque buildup on the teeth and gums. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth after eating or drinking, and if not removed through brushing and flossing, it can lead to a range of oral health problems. Other causes of oral diseases include poor nutrition, tobacco use, genetics, hormonal changes, and certain medications.
While bacteria naturally exist in the mouth, poor oral hygiene practices allow these bacteria to thrive, leading to the formation of plaque and tartar. Over time, these can cause gum irritation, tooth decay, and infections. Therefore, maintaining good oral hygiene and visiting your dentist regularly are essential for preventing oral diseases.
2. Common Oral Diseases
2.1 Tooth Decay (Cavities)
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or dental caries, is one of the most common oral diseases. It occurs when the enamel of the teeth becomes damaged due to acids produced by bacteria that feed on sugars and starches in food. These acids break down the tooth enamel, leading to holes or cavities in the teeth.
Symptoms of tooth decay include tooth sensitivity, pain when eating or drinking, and visible holes in the teeth. If left untreated, cavities can progress and affect the inner layers of the tooth, leading to more severe pain and the need for restorative treatments such as fillings or root canals.
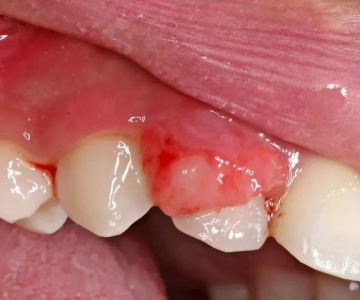
2.2 Gum Disease (Gingivitis and Periodontitis)
Gum disease is an infection of the tissues that surround and support the teeth. The two most common forms of gum disease are gingivitis and periodontitis.
2.2.1 Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the mildest form of gum disease and is characterized by inflammation and irritation of the gums. The primary cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene, which leads to the buildup of plaque on the teeth and gums. Symptoms of gingivitis include red, swollen gums that may bleed when brushing or flossing.
If caught early, gingivitis can be reversed with professional cleaning and improved home care. However, if left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis.
2.2.2 Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a more severe form of gum disease that can result from untreated gingivitis. It affects the deeper structures of the teeth, including the bone that supports them. Periodontitis can cause tooth mobility, gum recession, and even tooth loss if not properly managed.
Symptoms of periodontitis include persistent bad breath, gum recession, pockets between teeth and gums, and loose teeth. Treatment for periodontitis may involve deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), antibiotics, or, in some cases, surgery to restore damaged tissues.
2.3 Oral Cancer
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is a serious disease that can affect the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, and the roof and floor of the mouth. Risk factors for oral cancer include smoking, heavy alcohol use, and human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.
Symptoms of oral cancer include persistent sores, difficulty swallowing, unexplained weight loss, and a lump in the mouth or neck. Oral cancer can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated early, so it’s important to seek medical advice if you notice any of these signs.
2.4 Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity is a common problem that occurs when the protective enamel on your teeth wears away, exposing the sensitive underlying layer called dentin. This condition can cause discomfort or pain when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks.
The causes of tooth sensitivity can include gum recession, tooth decay, teeth grinding, and aggressive brushing. Treatment options include using desensitizing toothpaste, fluoride treatments, or dental procedures to cover exposed dentin and protect the teeth.
3. How to Prevent Oral Diseases
Oral diseases are largely preventable with good oral hygiene practices. Here are some effective ways to reduce the risk of developing oral health problems:
3.1 Brushing and Flossing
Brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily are essential for preventing tooth decay and gum disease. Brushing removes plaque from the surface of your teeth, while flossing cleans between your teeth where a toothbrush can't reach. Be sure to use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid damaging your gums and enamel.
3.2 Regular Dental Checkups
Visiting your dentist for regular checkups and professional cleanings is critical for maintaining oral health. Dentists can identify early signs of oral diseases such as cavities or gum disease, providing timely treatment to prevent further complications.
3.3 Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products can help keep your teeth and gums healthy. Limiting sugary snacks and drinks, which feed bacteria in the mouth, will also reduce your risk of developing cavities and gum disease.
3.4 Avoid Tobacco
Tobacco use, including smoking and chewing tobacco, is a leading cause of oral diseases, including gum disease and oral cancer. Quitting tobacco can significantly reduce your risk of these conditions and improve your overall oral health.
4. Treatment Options for Oral Diseases
Treatment for oral diseases depends on the severity of the condition. For example, early-stage tooth decay may be treated with a filling, while more advanced cases may require a root canal. Similarly, gingivitis can be treated with professional cleanings and improved oral hygiene, while periodontitis may require more intensive treatments, including scaling and root planing or even surgery.
If you suspect that you have an oral disease, it is essential to seek professional treatment as soon as possible. Early detection and intervention can prevent complications and improve the long-term outcome.
For personalized recommendations and the best oral care services, visit Dentistry Toothtruth to find expert advice and treatments for your oral health needs.



 Children's Dental FunZone - Pediatric Dentist & Orthodontist - Eagle Rock4.0 (1768 review)
Children's Dental FunZone - Pediatric Dentist & Orthodontist - Eagle Rock4.0 (1768 review) Dental Care at Estrella Crossroads4.0 (265 review)
Dental Care at Estrella Crossroads4.0 (265 review) Dr. Debbie L. Ashida, DDS4.0 (85 review)
Dr. Debbie L. Ashida, DDS4.0 (85 review) Maine Prosthodontics5.0 (168 review)
Maine Prosthodontics5.0 (168 review) Dental Minds4.0 (174 review)
Dental Minds4.0 (174 review) Smile For Life Dental5.0 (707 review)
Smile For Life Dental5.0 (707 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile