
Understanding the Risks of Untreated Periodontal Disease: Why You Should Take Action
- What is Periodontal Disease?
- Early Signs of Periodontal Disease
- Why Untreated Periodontal Disease is Dangerous
- Long-Term Complications of Periodontal Disease
- The Impact of Periodontal Disease on Overall Health
- Prevention and Treatment of Periodontal Disease
What is Periodontal Disease?
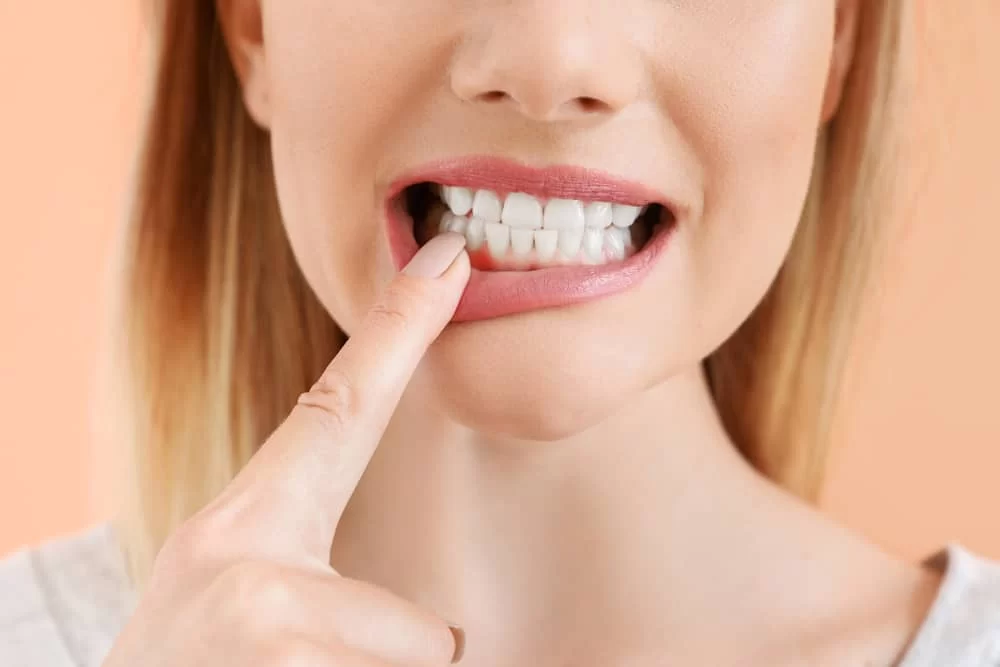
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a serious infection of the gums that can affect the tissues supporting your teeth. It typically starts as gingivitis, which causes the gums to become swollen and bleed easily. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease where the gums pull away from the teeth, creating pockets that harbor bacteria and can eventually lead to tooth loss.
Periodontal disease is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene, but other factors such as smoking, genetics, and certain health conditions like diabetes can increase your risk. It’s crucial to catch the disease in its early stages to prevent irreversible damage to your gums and teeth.
Early Signs of Periodontal Disease
Recognizing the early signs of periodontal disease is vital for preventing its progression. Some of the first indicators include:
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums: If your gums are easily irritated and bleed when brushing or flossing, it may be an early sign of gum disease.
- Persistent bad breath: Foul-smelling breath that doesn’t go away, even after brushing, could be a sign of an infection in your gums.
- Receding gums: When the gums start to pull away from the teeth, leaving them looking longer, it could indicate the beginning of periodontal disease.
- Sensitivity or discomfort while chewing: If chewing or brushing becomes painful, it could be a sign that the gums or underlying tissues are infected.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it's essential to seek dental care as soon as possible. Early intervention can help prevent the disease from advancing.
Why Untreated Periodontal Disease is Dangerous
If left untreated, periodontal disease can lead to severe and irreversible damage. Here’s why untreated gum disease is so dangerous:
1. Tooth Loss
One of the most common consequences of untreated periodontal disease is tooth loss. As the infection worsens, the gum tissue and bone supporting the teeth deteriorate. Eventually, teeth can become loose or fall out, requiring extraction or other dental procedures.
2. Increased Risk of Infections
As gum disease progresses, the bacteria in your gums can enter the bloodstream and spread to other parts of your body. This can lead to systemic infections that affect your heart, lungs, and other organs.
3. Bone Deterioration
In advanced stages of periodontal disease, the infection can cause bone loss in the jaw. This bone loss not only affects your teeth but can also impact your ability to eat and speak properly. In some cases, bone grafting procedures may be needed to restore lost bone structure.
4. Abscess Formation
Untreated gum disease can lead to the formation of abscesses, painful pockets of pus that develop in the gums. Abscesses are a sign of an active infection and require immediate attention to prevent them from spreading.
Long-Term Complications of Periodontal Disease
Beyond the immediate risks of gum disease, untreated periodontal disease can lead to serious long-term complications that affect both your oral health and overall well-being. Here are some of the potential long-term effects:
1. Heart Disease
There is growing evidence that untreated periodontal disease can increase your risk of heart disease. The bacteria from gum infections can enter your bloodstream, contributing to the development of plaque in your arteries, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
2. Diabetes Complications
People with diabetes are more susceptible to gum infections, and untreated periodontal disease can make it more difficult to manage blood sugar levels. In turn, poorly controlled diabetes can exacerbate gum disease, creating a vicious cycle.
3. Respiratory Problems
Infections from gum disease can spread to the lungs, leading to respiratory problems, especially in people with chronic lung conditions such as asthma or COPD. This can result in pneumonia or other lung infections.
4. Pregnancy Complications
Periodontal disease has been linked to premature births and low birth weights in pregnant women. The infection and inflammation associated with gum disease can affect the health of both the mother and the baby.
The Impact of Periodontal Disease on Overall Health
As the links between oral health and overall health become clearer, it’s important to realize that periodontal disease isn’t just a concern for your mouth. It’s a condition that can influence your entire body, increasing the risk of serious systemic health issues. Maintaining good periodontal health can improve your general well-being and reduce the chances of developing conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory problems.
Therefore, taking care of your gums and seeking treatment for periodontal disease as soon as symptoms arise is vital for both your oral and overall health.
Prevention and Treatment of Periodontal Disease
The best way to prevent periodontal disease is through regular dental checkups, proper brushing, and flossing techniques. Professional cleanings can remove plaque buildup that may otherwise lead to gum disease.
If you have already developed periodontal disease, early treatment can help stop its progression and reduce the risks of long-term damage. Treatment options may include:
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from beneath the gum line, smoothing the root surfaces to encourage reattachment of the gums to the teeth.
- Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to treat infections and reduce bacteria in the gums.
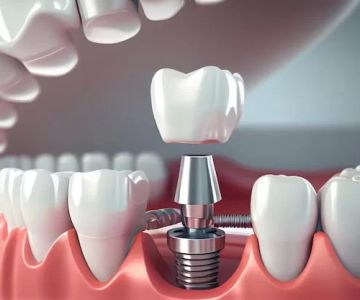
- Surgical Treatments: In more severe cases, surgical options such as flap surgery or bone grafts may be required to restore gum and bone health.
If you suspect you have periodontal disease, it's essential to visit your dentist as soon as possible to avoid these severe complications. The sooner you address the issue, the better the chances of preserving your oral health.




 Marc Weinberger, D.M.D.4.0 (17 review)
Marc Weinberger, D.M.D.4.0 (17 review) Dooley Dental: Edward J Dooley DMD, Dr Robert Scheddin DMD4.0 (162 review)
Dooley Dental: Edward J Dooley DMD, Dr Robert Scheddin DMD4.0 (162 review) Dr. Guzman Dental Office4.0 (18 review)
Dr. Guzman Dental Office4.0 (18 review) NJ Periodontics & Dental Implants5.0 (10 review)
NJ Periodontics & Dental Implants5.0 (10 review) Crown Point Dental Care4.0 (453 review)
Crown Point Dental Care4.0 (453 review) Sumner Smiles Dentistry4.0 (79 review)
Sumner Smiles Dentistry4.0 (79 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile