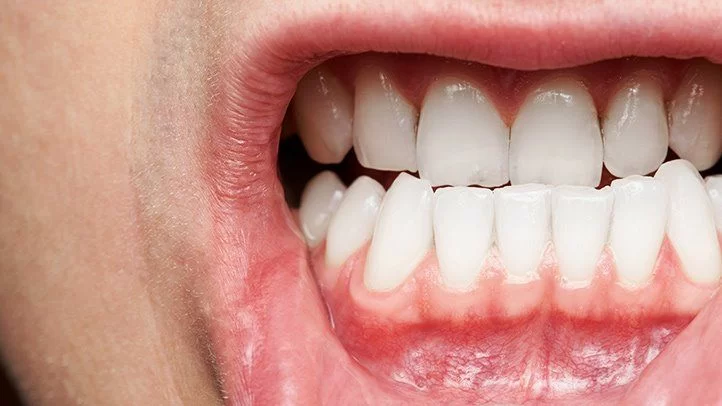
Understanding the Link Between Gum Disease and Diabetes: How Oral Health Affects Diabetes
- Introduction
- The Link Between Gum Disease and Diabetes
- How Diabetes Affects Oral Health
- Symptoms of Gum Disease in Diabetics
- Managing Gum Disease in Diabetes
- Conclusion
For those living with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is essential for overall health. However, many people don't realize that diabetes also significantly affects oral health. One of the most common oral health issues for diabetics is gum disease, which can lead to a variety of complications if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the link between gum disease and diabetes, how diabetes impacts oral health, and what you can do to maintain healthy gums despite diabetes.
The Link Between Gum Disease and Diabetes
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the gums that can damage the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. It's more common in people with diabetes due to the body's reduced ability to fight infections when blood sugar levels are high. Additionally, high blood sugar can promote the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth, leading to infections and gum inflammation.
On the other hand, gum disease can also make it more difficult for diabetics to control their blood sugar levels. Inflammation caused by gum disease can contribute to insulin resistance, making it harder for the body to use insulin effectively. This creates a vicious cycle where uncontrolled diabetes worsens gum disease, and severe gum disease makes it harder to manage diabetes.
How Diabetes Affects Oral Health
Diabetes affects oral health in several ways. The most direct impact is on the body's ability to fight infections, including those in the gums. High blood sugar levels weaken the immune system, making it harder to combat bacteria and inflammation in the mouth. Additionally, diabetes can lead to dry mouth, a condition where the salivary glands don't produce enough saliva. This dryness can promote bacterial growth and further contribute to the development of gum disease.
Another significant concern for diabetics is the higher likelihood of developing tooth decay. Elevated glucose levels can cause sugar to accumulate in the mouth, providing food for bacteria that cause cavities. Furthermore, diabetes can also delay the body's ability to heal, which means gum injuries or infections may take longer to recover.
Symptoms of Gum Disease in Diabetics
People with diabetes should be particularly vigilant about their oral health. Gum disease can be subtle in its early stages, so it's essential to know the signs and symptoms to look for. Some common symptoms of gum disease include:
- Gums that are red, swollen, or bleed when brushing or flossing
- Bad breath that doesn’t go away
- Receding gums or pockets forming between the teeth and gums
- Loose teeth or changes in bite
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to visit a dentist as soon as possible to prevent further complications.
Managing Gum Disease in Diabetes
Managing gum disease is crucial for people with diabetes to maintain both their oral health and overall well-being. Here are some tips for managing gum disease if you have diabetes:
1. Control Your Blood Sugar
Keeping your blood sugar levels within the target range is one of the best ways to protect your gums and teeth. Stable blood sugar helps prevent the overgrowth of bacteria in the mouth and reduces inflammation in the gums.
2. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles. Regular oral care can help reduce the buildup of harmful bacteria that cause gum disease. Additionally, using an antibacterial mouthwash can further reduce bacteria and inflammation.
3. Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Routine dental checkups are essential for preventing gum disease. Your dentist can detect early signs of gum disease and provide professional cleaning to remove tartar buildup. They can also offer advice on how to improve your oral care routine at home.
4. Stay Hydrated
Diabetes can lead to dry mouth, so it’s essential to drink plenty of water throughout the day. Staying hydrated helps promote saliva production, which helps wash away food particles and bacteria in the mouth.
Conclusion
There is a clear link between gum disease and diabetes, and managing both conditions is essential for maintaining your overall health. By controlling your blood sugar, maintaining good oral hygiene, visiting your dentist regularly, and staying hydrated, you can help prevent and manage gum disease effectively. If you're concerned about gum disease or diabetes, speak with your dentist or healthcare provider to develop a personalized care plan. For more information on how to protect your teeth from grinding and other oral health concerns, visit Dentistry Toothtruth.




 Rose & Hollander Dental Associates4.0 (45 review)
Rose & Hollander Dental Associates4.0 (45 review) Ocean County Endodontics LLC: Mc Cafferty Ryan J DDS4.0 (8 review)
Ocean County Endodontics LLC: Mc Cafferty Ryan J DDS4.0 (8 review) North Shore Smiles Pediatric Dentistry5.0 (52 review)
North Shore Smiles Pediatric Dentistry5.0 (52 review) Samantha H Roach, DDS, MS5.0 (26 review)
Samantha H Roach, DDS, MS5.0 (26 review) Matawan Dental Galleria5.0 (307 review)
Matawan Dental Galleria5.0 (307 review) Central Park Dental Aesthetics4.0 (129 review)
Central Park Dental Aesthetics4.0 (129 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile