Gum Disease: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Periodontal Health
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health issue affecting millions across the United States. Dentistry Toothtruth provides insights and resources to help manage this silent yet impactful condition. Understanding its causes, progression, and prevention can significantly improve both oral and systemic health.
Causes of Gum Disease
The primary cause of gum disease is the accumulation of plaque—a sticky, colorless film of bacteria that forms constantly on teeth. If not removed, it can harden into tartar, leading to various periodontal problems. Other factors can exacerbate the condition, including smoking, uncontrolled diabetes, and genetic predisposition.
Stages of Gum Disease
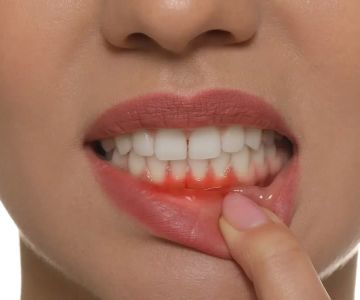
Gum disease typically starts as gingivitis, characterized by inflammation and bleeding of the gums. Without intervention, it can progress to periodontitis, where the inner layer of the gum and bone pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. Advanced stages result in the destruction of the supporting bone and tissue structures.
Identifying Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms early is crucial. Common signs include swollen or bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, and loose or shifting teeth. Regular dental check-ups can aid in early diagnosis, preventing the progression to more severe forms.
Impact on Health
Research indicates a significant correlation between gum disease and systemic health issues such as cardiovascular diseases, stroke, and diabetes. Addressing periodontal health is not only crucial for oral hygiene but also for reducing risks associated with these chronic conditions.
Prevention Strategies
Preventive measures are effective in managing gum health. These include brushing twice daily, flossing, using an antiseptic mouthwash, and attending regular dental cleanings. Adopting a healthy lifestyle by quitting smoking and eating a balanced diet also plays a vital role.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage of gum disease. Non-surgical approaches include scaling and root planing, while surgical interventions may be necessary for advanced cases. Medications, such as antibiotics, may also assist in controlling infection.
Summarizing, gum disease is a prevalent yet preventable condition. By understanding its nature and implementing effective prevention and treatment strategies, individuals can ensure better oral and overall health. For more expert advice and resources, visit Dentistry Toothtruth today.






 Village Dental - North Raleigh4.0 (1577 review)
Village Dental - North Raleigh4.0 (1577 review) West Coast Dental of Van Nuys4.0 (318 review)
West Coast Dental of Van Nuys4.0 (318 review) Acworth Smiles Dentistry4.0 (145 review)
Acworth Smiles Dentistry4.0 (145 review) Susan J. Curley, DDS4.0 (282 review)
Susan J. Curley, DDS4.0 (282 review) Don Swearingen5.0 (18 review)
Don Swearingen5.0 (18 review) Parkside Family Dental4.0 (276 review)
Parkside Family Dental4.0 (276 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile