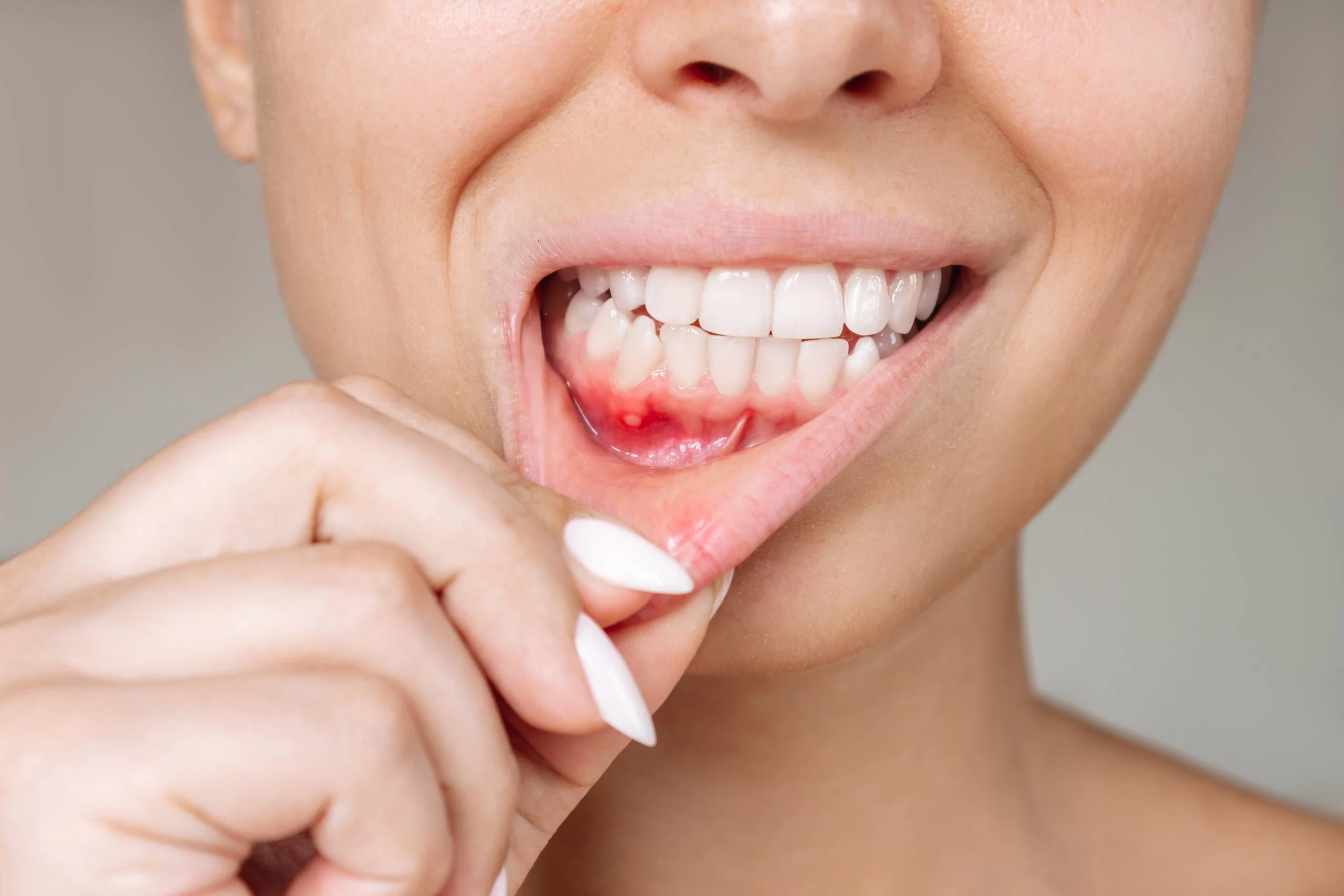

Symptoms of a Gum Infection and Treatment
- Understanding Gum Infections
- Signs and Symptoms of a Gum Infection
- What Causes Gum Infections?
- Treatment Options for Gum Infections
- How to Prevent Gum Infections
- Real-Life Experience and Expert Tips
Understanding Gum Infections
A gum infection is an inflammation or infection of the tissues surrounding your teeth, commonly caused by poor oral hygiene. When plaque builds up along the gumline, it can cause irritation and infection in the gums. If left untreated, it may lead to more severe conditions, such as periodontal disease or tooth loss.
Understanding the symptoms of a gum infection is crucial for early detection and treatment, preventing complications like tooth loss or chronic gum disease.
Signs and Symptoms of a Gum Infection
It’s important to identify the signs of a gum infection early, as it can worsen without proper treatment. Here are some common symptoms:
- Red, Swollen Gums: The gums may appear redder than usual, and they may swell as a result of infection.
- Bleeding Gums: One of the most common signs of a gum infection is bleeding, especially when brushing or flossing your teeth.
- Pain or Tenderness: You might feel pain or discomfort when chewing or touching the affected area.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath or a foul taste in your mouth can indicate an infection.
- Receding Gums: In some cases, the gums may begin to recede, exposing more of your teeth or even the tooth’s root.
- Loose Teeth: Advanced gum infections can cause the teeth to become loose or shift in position.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to schedule a dental appointment as soon as possible to prevent the infection from worsening.
What Causes Gum Infections?
Gum infections are typically caused by bacterial buildup from plaque. However, several factors can contribute to the development of gum infections:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Failure to brush and floss regularly allows plaque to accumulate and irritate the gums.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Smoking weakens the immune system and reduces blood flow to the gums, making it easier for infections to develop.
- Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to gum disease, even with good oral hygiene.
- Medications: Certain medications can reduce saliva production, which can lead to dry mouth and a higher risk of gum infections.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to infection.
Identifying the underlying cause of a gum infection is key to finding the most effective treatment and reducing the risk of future infections.
Treatment Options for Gum Infections
If you have a gum infection, there are several treatment options available depending on the severity of the infection:
- Professional Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing): For mild infections, your dentist may perform a deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup beneath the gumline.
- Antibiotics: In cases of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to help eliminate bacteria causing the infection.
- Gum Surgery: For advanced gum disease, surgery such as flap surgery or soft tissue grafts may be required to restore the gumline.
- Antiseptic Rinses: Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in the mouth and promote gum healing.
For minor infections, treating the infection early with a dentist’s help can often prevent the need for more invasive treatments.
How to Prevent Gum Infections
Prevention is the best way to protect your gums and teeth from infections. Here are some effective strategies to keep your gums healthy:
- Brush Twice a Day: Brush your teeth for at least two minutes using fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque buildup.
- Floss Daily: Flossing helps to remove food particles and plaque from between the teeth and along the gumline.
- Use an Antiseptic Mouthwash: A mouthwash with antimicrobial properties can help reduce bacteria in your mouth.
- Regular Dental Visits: See your dentist for regular checkups and professional cleanings to catch infections early.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking weakens the immune system and hinders gum healing, so quitting can significantly reduce the risk of gum infections.
By maintaining a good oral hygiene routine and making regular dental visits, you can significantly reduce the risk of gum infections.
Real-Life Experience and Expert Tips
I recently had a patient, Sarah, who came to me complaining about persistent bad breath and swollen gums. After examining her, I discovered she had a gum infection that had developed due to poor oral hygiene and smoking. Fortunately, we were able to treat the infection with scaling and root planing, followed by a course of antibiotics. Sarah was given a personalized oral care plan, and after a few months, her gums were much healthier, and the infection had cleared up.
Expert tip: If you experience gum pain, redness, or bleeding, don’t wait. Visit your dentist as soon as possible to avoid more serious complications. Early treatment can save your gums and teeth from long-term damage.
If you want to learn more about preventing or treating gum infections, check out Dentistry Toothtruth for expert advice and products tailored to oral health.







 Tai K. Mao, DDS., Pinnacle Dental Care4.0 (101 review)
Tai K. Mao, DDS., Pinnacle Dental Care4.0 (101 review) Sperling Dental4.0 (55 review)
Sperling Dental4.0 (55 review) Heritage Grove Family Dental - Plainfield Dental Clinic4.0 (1397 review)
Heritage Grove Family Dental - Plainfield Dental Clinic4.0 (1397 review) Smile For All Family Dental0.0 (0 review)
Smile For All Family Dental0.0 (0 review) Richards & Associates Orthodontics4.0 (228 review)
Richards & Associates Orthodontics4.0 (228 review) Comfort Dental North Powers4.0 (914 review)
Comfort Dental North Powers4.0 (914 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile