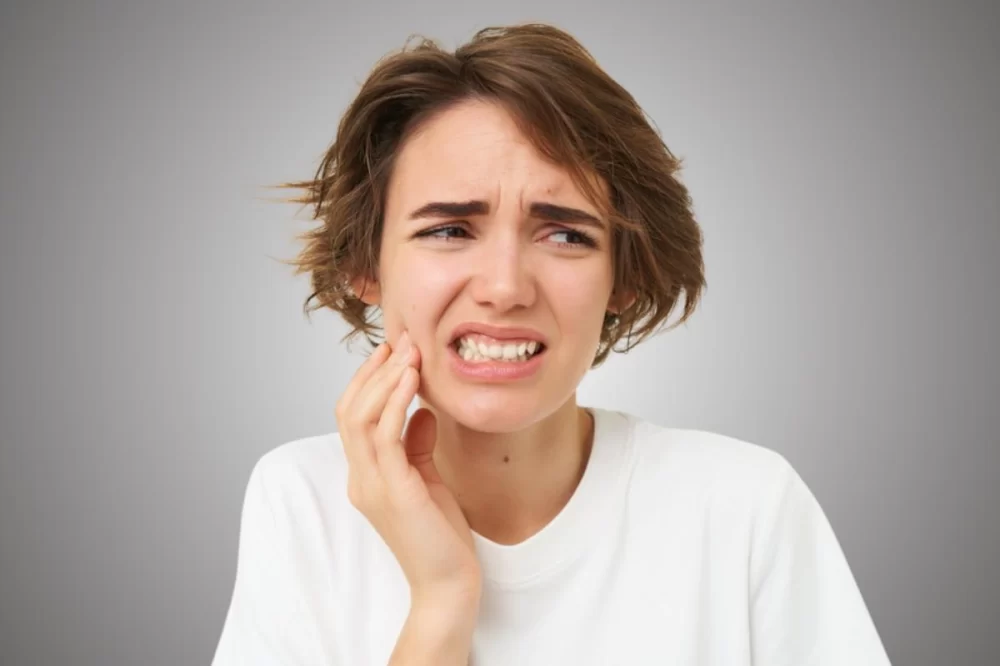

- Understanding Tooth Infection: Causes and Development
- Common Signs of Tooth Infection Symptoms and What They Mean
- When to Seek Emergency Care for Tooth Infection
- Real-Life Case Studies Illustrating Tooth Infection Dangers
- Professional Advice and Prevention Tips
- How Dentistry Toothtruth Can Help with Treatment and Care
1. Understanding Tooth Infection: Causes and Development
Tooth infections, medically referred to as dental abscesses, occur when bacteria invade the inner parts of the tooth, including the pulp where nerves and blood vessels reside. This invasion usually stems from untreated cavities, cracked teeth, or injuries that allow bacteria to penetrate the protective enamel. Over time, the infection can spread beyond the tooth into the gums, jawbone, and other facial structures if not promptly treated.
The development of a tooth infection is often gradual. Initially, bacteria multiply inside the pulp, causing inflammation and pressure buildup, which results in pain. If left unchecked, this pressure can cause the pulp to die and the infection to spread, creating pus pockets that further intensify discomfort and swelling.
Understanding this progression is crucial because early intervention can prevent severe complications. The bacteria from a dental infection can even enter the bloodstream, potentially leading to life-threatening conditions such as sepsis. Therefore, recognizing early symptoms is a critical step toward maintaining oral and overall health.
1.1 Common Causes Leading to Tooth Infection
Most tooth infections originate from:
- Deep untreated cavities caused by poor dental hygiene
- Cracked or broken teeth exposing the pulp
- Recent dental procedures that may have introduced bacteria
- Gum disease that causes pockets of infection around teeth
1.2 The Role of the Immune System
The body’s immune response to bacterial invasion can cause swelling, redness, and pain. Sometimes this response creates an abscess that contains pus—a sign the body is trying to fight off the infection. However, the abscess itself can be dangerous, requiring professional dental intervention.
2. Common Signs of Tooth Infection Symptoms and What They Mean
Identifying the signs of a tooth infection early can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. These symptoms often escalate, so being attentive can prevent the need for emergency care.
2.1 Early Symptoms
Initial signs may include mild to moderate toothache that worsens when chewing or applying pressure. Sensitivity to hot or cold stimuli often indicates that the nerve inside the tooth is irritated.
2.2 Advanced Symptoms
As the infection progresses, symptoms can intensify and include:
- Severe, throbbing pain that may radiate to the jaw, ear, or neck
- Swelling of the gums or face
- Redness and tenderness in the affected area
- Formation of a pimple-like bump on the gums, which may leak pus
- Fever or general feeling of being unwell, indicating systemic infection
2.3 Less Obvious Signs
Sometimes, patients report bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth, which can be a subtle indication of infection. Difficulty swallowing or opening the mouth widely are more serious signs of infection spread and warrant urgent care.
3. When to Seek Emergency Care for Tooth Infection
Recognizing when to seek emergency care is vital. Not every toothache requires urgent attention, but certain symptoms should never be ignored.
3.1 Immediate Emergency Warning Signs
If you experience any of the following, seek emergency dental care immediately:
- Rapidly increasing swelling that affects breathing or swallowing
- High fever accompanied by chills
- Severe facial swelling extending beyond the immediate area of the tooth
- Intense pain unrelieved by over-the-counter medication
- Confusion or disorientation (signs that infection may have spread)
3.2 Why Emergency Care Matters
Emergency care for tooth infections often involves draining abscesses, prescribing antibiotics, and sometimes urgent dental procedures such as root canals or tooth extraction. Prompt treatment not only alleviates pain but also prevents the infection from spreading to critical areas like the sinuses or brain.
4. Real-Life Case Studies Illustrating Tooth Infection Dangers
To highlight the importance of early recognition and treatment, consider the story of Sarah, a 32-year-old woman who ignored mild tooth pain for weeks. What started as slight discomfort turned into severe facial swelling and fever. By the time she sought care, the infection had spread to her jawbone, requiring hospitalization and surgery. Sarah’s experience underscores the critical nature of timely dental attention.
Another case involved a young man named Mike, whose tooth infection led to difficulty breathing due to swelling in the throat. Emergency intervention saved his life, illustrating how dental infections can escalate beyond a simple toothache.
5. Professional Advice and Prevention Tips
Preventing tooth infections begins with proper oral hygiene—brushing twice daily, flossing, and regular dental checkups. Avoiding sugary foods and drinks that promote decay is also essential.
If you notice any early symptoms, don’t delay consulting a dentist. Early treatments like fillings or root canal therapy can stop infections before they worsen.
5.1 Role of Antibiotics and Dental Procedures
Antibiotics are important for controlling infection, but they are not a standalone cure. Definitive dental treatment to remove the infection source is necessary. Therefore, antibiotics should always be followed by appropriate dental care.
5.2 Long-Term Oral Health Strategies
Maintaining good oral health routines and scheduling regular dental visits can reduce the risk of future infections. Educating yourself about signs of tooth infection symptoms also empowers timely action.
6. How Dentistry Toothtruth Can Help with Treatment and Care
For those seeking trusted dental solutions and professional guidance, Dentistry Toothtruth offers a comprehensive range of services tailored to treat tooth infections and related emergencies. Whether you need urgent care, preventive advice, or specialized dental products, Dentistry Toothtruth can connect you with the most appropriate resources.
Their expert team emphasizes patient education, ensuring you understand your condition and treatment options clearly, helping reduce anxiety and improve outcomes. When facing any dental concern, including signs of tooth infection symptoms and emergency care needs, Dentistry Toothtruth is a reliable partner to guide you toward healthy, pain-free living.







 West Dundee Dental4.0 (33 review)
West Dundee Dental4.0 (33 review) Dr. Maha Blaibel, DDS5.0 (6 review)
Dr. Maha Blaibel, DDS5.0 (6 review) Northborough Dental Associates4.0 (261 review)
Northborough Dental Associates4.0 (261 review) Access Dental, Dentures & Implants4.0 (426 review)
Access Dental, Dentures & Implants4.0 (426 review) Pearl Family Dental Care4.0 (123 review)
Pearl Family Dental Care4.0 (123 review) Hutchinson Metro Dental4.0 (2685 review)
Hutchinson Metro Dental4.0 (2685 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile