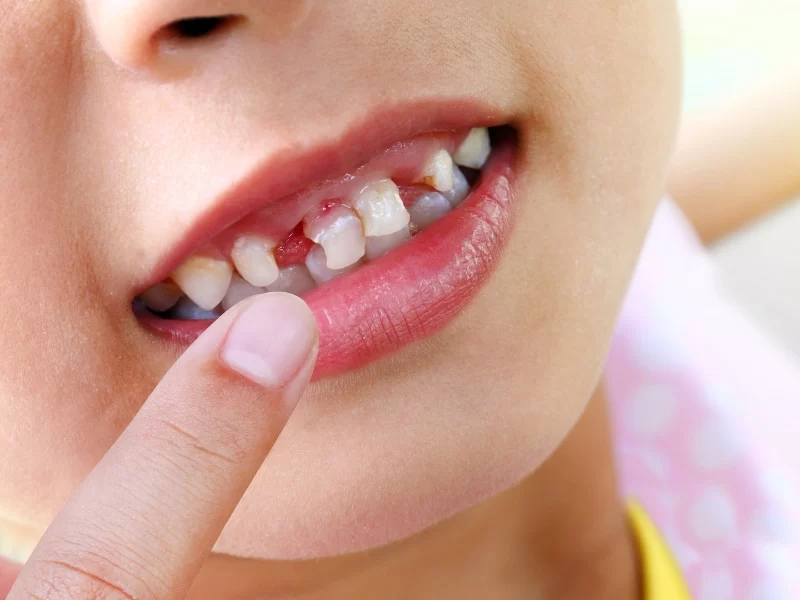

- Understanding Oral Inflammation in Children
- Common Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
- Causes Behind Oral Inflammation in Young Kids
- When to Seek Professional Help
- Real-Life Example of Early Detection and Treatment
- Tips for Preventing Oral Inflammation in Children
- Resources and Products for Pediatric Oral Health
1. Understanding Oral Inflammation in Children
Oral inflammation in children refers to the swelling, redness, and irritation of oral tissues, including gums, cheeks, tongue, and the roof of the mouth. This condition is relatively common but can sometimes be overlooked because young children might not clearly express discomfort. Recognizing the early signs of oral inflammation in children is essential for preventing more serious dental problems such as infections, tooth decay, or gum disease.
Unlike adults, children’s mouths are still developing, which makes them more susceptible to inflammation due to sensitive tissue and emerging teeth. Parents and caregivers need a clear understanding of how oral inflammation manifests in kids to take timely action and protect their child’s oral health.
1.1 Why Early Recognition Matters
Ignoring mild oral inflammation can lead to complications, including pain, difficulty eating, or spreading infection. Early detection allows for simple treatments that can avoid invasive procedures later on, helping maintain a child’s comfort and healthy development.
1.2 Differentiating Between Normal Irritation and Inflammation
It’s important to distinguish between temporary irritations — like those from a rough tooth brushing — and true inflammation that signals an underlying problem. Signs that go beyond mild redness, such as persistent swelling or bleeding, warrant closer attention.
2. Common Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Identifying signs of oral inflammation in children requires observation and some knowledge of typical symptoms. Here are the most common indicators parents should watch for:
2.1 Redness and Swelling
One of the first visible signs is redness around the gums or inside the cheeks. Swelling can make the tissues appear puffier than usual and may cause tenderness.
2.2 Bleeding Gums
Bleeding during or after brushing or flossing is a warning sign that gums might be inflamed. While occasional minor bleeding can happen, frequent bleeding should not be ignored.
2.3 Pain or Sensitivity
Children might express discomfort when eating hot, cold, or sweet foods. They may also resist tooth brushing due to sensitivity.
2.4 Bad Breath and Unusual Taste
Persistent bad breath or a strange taste in the mouth can accompany inflammation caused by bacterial buildup or infection.
2.5 Behavioral Changes
Young children might become irritable, have trouble eating, or show reluctance to open their mouths when oral inflammation causes discomfort.
3. Causes Behind Oral Inflammation in Young Kids
Understanding why oral inflammation occurs helps in prevention and treatment. Several factors contribute to inflammation in children’s mouths:
3.1 Poor Oral Hygiene
Insufficient brushing and flossing allow plaque buildup, which irritates gums and soft tissues.
3.2 Viral or Bacterial Infections
Common infections such as hand, foot, and mouth disease or oral thrush can cause inflammation.
3.3 Teething Discomfort
As new teeth emerge, the gums can become tender and inflamed, a natural but sometimes uncomfortable process.
3.4 Allergies and Irritants
Reactions to toothpaste ingredients, foods, or environmental allergens can trigger inflammation.
4. When to Seek Professional Help
While some mild cases of oral inflammation may resolve with home care, certain situations require immediate dental attention:
4.1 Persistent or Worsening Symptoms
If redness, swelling, or pain does not improve within a few days or gets worse, a dental professional should evaluate the child.
4.2 Difficulty Eating or Drinking
When inflammation impairs a child’s ability to eat, causing dehydration or weight loss, prompt care is essential.
4.3 Signs of Infection
Fever, pus, or severe swelling around the mouth indicates infection that needs urgent treatment.
5. Real-Life Example of Early Detection and Treatment
Consider Liam, a 5-year-old whose parents noticed his gums were unusually red and he became reluctant to eat his favorite snacks. Initially dismissed as a passing phase, the symptoms persisted and worsened over a week. A visit to their dentist revealed early gum inflammation caused by plaque accumulation due to inconsistent brushing habits. With professional cleaning and a tailored oral hygiene routine, Liam’s condition improved quickly, and he regained comfort and appetite.
Liam’s story emphasizes the importance of observing signs of oral inflammation in children and seeking timely professional advice. Early intervention can save children from discomfort and more serious dental problems.
6. Tips for Preventing Oral Inflammation in Children
Preventive care is the best strategy to avoid oral inflammation. Parents and caregivers can adopt these practical tips:
6.1 Establish a Consistent Oral Hygiene Routine
Encourage brushing twice daily with child-friendly toothpaste and flossing as soon as teeth start touching. Make oral care fun and rewarding to build good habits.
6.2 Monitor Diet and Limit Sugary Foods
Sugary snacks and drinks promote bacterial growth, which increases the risk of inflammation.
6.3 Regular Dental Checkups
Schedule routine visits to the dentist every six months for preventive care and early detection.
6.4 Use Appropriate Oral Care Products
Choose mild, fluoride-containing toothpaste and soft-bristled toothbrushes designed for children to minimize irritation.
7. Resources and Products for Pediatric Oral Health
For families looking for reliable oral care solutions and professional advice, Dentistry Toothtruth offers a wide selection of child-friendly dental products and expert services. Whether you need gentle toothbrushes, safe toothpaste options, or guidance on pediatric oral health, their resources are designed to support parents in maintaining their children’s healthy smiles.
By utilizing these trusted products and services, caregivers can confidently manage and prevent signs of oral inflammation in children, ensuring lasting oral health from an early age.







 Family Orthodontics - Peachtree City4.0 (134 review)
Family Orthodontics - Peachtree City4.0 (134 review) Community Health Care Hilltop Family Dental Clinic3.0 (188 review)
Community Health Care Hilltop Family Dental Clinic3.0 (188 review) Wai Kahala Dentistry LLC5.0 (43 review)
Wai Kahala Dentistry LLC5.0 (43 review) Gentle Dental Service4.0 (113 review)
Gentle Dental Service4.0 (113 review) Little Big Smiles Pediatric Dentistry of Fort Myers5.0 (130 review)
Little Big Smiles Pediatric Dentistry of Fort Myers5.0 (130 review) Brinton Family Dentistry4.0 (469 review)
Brinton Family Dentistry4.0 (469 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile