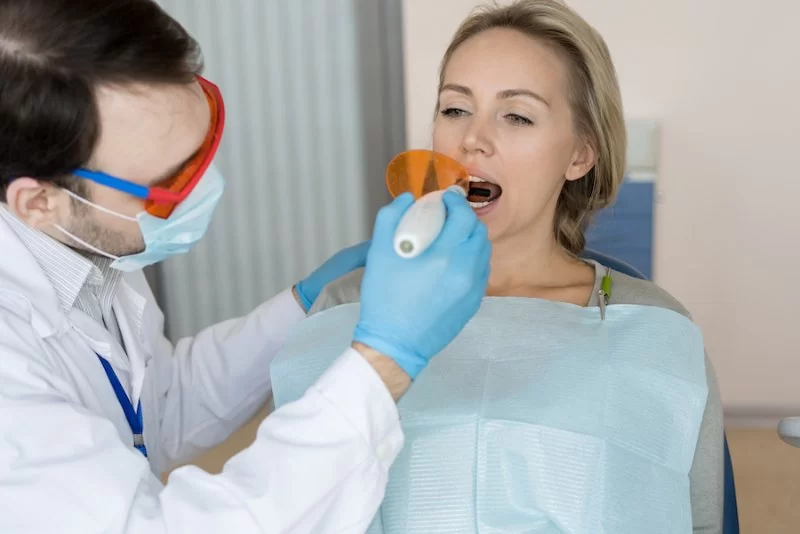
How to Treat Receding Gums: Treatment Options and Prevention
- 1 - Understanding Receding Gums
- 2 - Common Causes of Receding Gums
- 3 - Treatment Options for Receding Gums
- 4 - Tips for Preventing Receding Gums
- 5 - When to See a Dentist for Receding Gums
1 - Understanding Receding Gums
Receding gums is a common dental condition where the gum tissue that surrounds the teeth pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or the tooth's root. While it may seem like a cosmetic issue, receding gums can lead to serious dental problems, such as tooth sensitivity, increased risk of decay, and even tooth loss. Understanding how receding gums occur is the first step in preventing and treating the condition. In the early stages, it may not be obvious, but with time, it can progress and affect overall oral health.
2 - Common Causes of Receding Gums
Receding gums can be caused by a variety of factors. The most common causes include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Lack of proper brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup along the gumline, which can irritate the gums and cause them to recede.
- Gum Disease: Gingivitis and periodontitis, the two main stages of gum disease, can contribute significantly to gum recession if left untreated.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to gum recession, making them more susceptible.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menopause, and puberty can all affect the health of your gums.
- Brushing Too Hard: Brushing with excessive force or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can wear down the gums over time.
By understanding the underlying causes, it becomes easier to take proactive steps in preventing and treating receding gums.
3 - Treatment Options for Receding Gums
If you notice signs of gum recession, it's essential to seek treatment as soon as possible. There are several treatment options available depending on the severity of the condition:
- Non-Surgical Treatments: For early-stage gum recession, non-surgical treatments such as deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) and antimicrobial treatments may help prevent further recession and promote gum health.
- Gum Grafting: In more advanced cases, a gum graft may be needed. This procedure involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth and attaching it to the affected area to restore the gumline.
- Flap Surgery: For severe cases, flap surgery may be necessary to clean the roots of the teeth and restore the gum tissue.
It's important to consult with a dental professional to determine the most suitable treatment based on your specific situation.
4 - Tips for Preventing Receding Gums
Prevention is always better than treatment. Here are some helpful tips to prevent receding gums:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush, and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent gum disease.
- Use a Mouthwash: Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria in your mouth and prevent gum disease.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Regular dental checkups can help detect early signs of gum disease and other oral health issues.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease and can contribute to gum recession.
- Wear a Nightguard: If you grind your teeth, wearing a nightguard can prevent damage to your gums and teeth.
By following these preventive measures, you can maintain healthy gums and reduce the risk of receding gums.
5 - When to See a Dentist for Receding Gums
If you notice any of the following symptoms, it's time to consult a dentist:
- Visible gum recession or a tooth that looks longer than before.
- Tooth sensitivity to hot or cold.
- Bleeding or swollen gums after brushing or flossing.
- Bad breath or a persistent bad taste in your mouth.
Early intervention is key to preventing further damage and improving oral health. A dentist can recommend the best course of action to treat your receding gums.
If you're looking for more information about oral health products, services, or treatments, visit Family Dentistry Online for tailored recommendations that can help you maintain your smile!







 Kocian Family Dental5.0 (486 review)
Kocian Family Dental5.0 (486 review) Fifth Avenue Dental4.0 (750 review)
Fifth Avenue Dental4.0 (750 review) Dr. Backiel and Associates4.0 (213 review)
Dr. Backiel and Associates4.0 (213 review) Uncasville Dental Associates4.0 (103 review)
Uncasville Dental Associates4.0 (103 review) Little Big Smiles Pediatric Dentistry of Fort Myers5.0 (130 review)
Little Big Smiles Pediatric Dentistry of Fort Myers5.0 (130 review) Lindsey Anderson Family Dentistry4.0 (85 review)
Lindsey Anderson Family Dentistry4.0 (85 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile