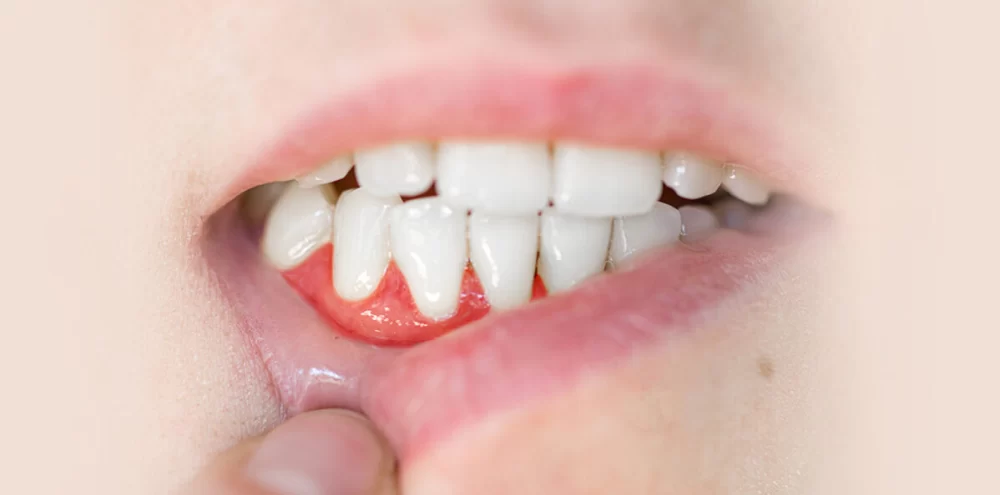
How to Reduce Gum Swelling from Tooth Disease: Effective Treatments and Tips
- 1-Understanding Gum Swelling and Tooth Disease
- 2-Causes of Gum Swelling Due to Tooth Disease
- 3-Treatment Options for Reducing Gum Swelling
- 4-Home Remedies for Gum Swelling Relief
- 5-Prevention Tips for Gum Health
- 6-When to See a Dentist for Gum Swelling
1. Understanding Gum Swelling and Tooth Disease
Gum swelling, often linked with tooth disease, can be a painful and concerning issue. It occurs when the gums become inflamed due to infection or irritation, often due to bacteria, plaque buildup, or dental issues like cavities or gingivitis. The condition can lead to discomfort, bleeding, and bad breath. Understanding the root causes and symptoms of gum swelling can help you take the necessary steps to manage the condition and improve your overall oral health.
2. Causes of Gum Swelling Due to Tooth Disease
There are several reasons why tooth disease can lead to gum swelling. The most common causes include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Bacteria from plaque buildup can irritate the gums and lead to infection.
- Gingivitis: This early-stage gum disease is characterized by gum inflammation and can result from insufficient brushing and flossing.
- Tooth Infection: A bacterial infection in the tooth can spread to the surrounding gum tissue, causing swelling.
- Abscessed Teeth: An abscess, which is a pus-filled pocket caused by bacterial infection, can cause severe swelling and pain in the gums.
Identifying the specific cause of your gum swelling is crucial for determining the right treatment approach.
3. Treatment Options for Reducing Gum Swelling
To reduce gum swelling effectively, you should consider the following treatment options:
- Antibiotics: If the swelling is caused by an infection, antibiotics prescribed by a dentist can help eliminate the bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Deep Cleaning: A dental professional may perform a deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) to remove plaque and tartar buildup from the gum line.
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and swelling.
- Gum Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove damaged tissue and restore gum health.
These treatments are usually determined based on the severity of the gum swelling and the underlying cause of the tooth disease.
4. Home Remedies for Gum Swelling Relief
If you're looking for natural ways to manage gum swelling at home, there are several remedies you can try:
- Salt Water Rinse: Gargling with warm salt water can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the swollen area can reduce swelling and numb the pain.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe irritated gums.
- Essential Oils: Peppermint or tea tree oil diluted in water can be used as a mouth rinse to fight bacteria and reduce swelling.
While these remedies can provide temporary relief, they should not replace professional dental care if the problem persists.
5. Prevention Tips for Gum Health
Prevention is always better than cure. To maintain healthy gums and prevent swelling, follow these essential tips:
- Brush Regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day to remove plaque and prevent gum disease.
- Floss Daily: Flossing helps remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth and gums.
- Use Mouthwash: An antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce plaque buildup and fight bacteria.
- Visit Your Dentist: Regular dental checkups can help catch gum disease early before it causes serious issues.
Incorporating these practices into your daily routine can significantly reduce the risk of gum swelling caused by tooth disease.
6. When to See a Dentist for Gum Swelling
If your gum swelling persists despite home remedies, or if you experience severe pain, fever, or pus, it's essential to see a dentist promptly. These could be signs of a more serious infection, such as an abscess or advanced gum disease, requiring professional treatment to prevent further complications.







 Palm Valley Orthodontics5.0 (3 review)
Palm Valley Orthodontics5.0 (3 review) Austin Dental Associates4.0 (139 review)
Austin Dental Associates4.0 (139 review) Aspen Dental - Philadelphia, PA4.0 (326 review)
Aspen Dental - Philadelphia, PA4.0 (326 review) Taher Family Dental5.0 (161 review)
Taher Family Dental5.0 (161 review) Smile For Life Dental5.0 (707 review)
Smile For Life Dental5.0 (707 review) Star Pediatric Dentistry of Point Pleasant5.0 (164 review)
Star Pediatric Dentistry of Point Pleasant5.0 (164 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile