Does Barium Sulfate Oral Check Kidney Function? An In-Depth Explanation
Barium sulfate is a compound commonly used in medical imaging, particularly in procedures like X-rays and CT scans. While it is well-known for its role in visualizing the gastrointestinal tract, many patients wonder if barium sulfate can be used to check kidney function. This article will delve into the details of how barium sulfate is used in diagnostic imaging, its role in kidney health assessments, and alternative methods for evaluating kidney function.
The Role of Barium Sulfate in Medical Imaging
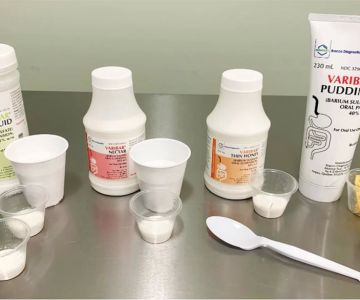
Barium sulfate is often used as a contrast agent in radiology. It is most commonly administered orally or as an enema to improve the visibility of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract during X-rays or CT scans. When ingested, barium sulfate absorbs X-rays and appears white on the scan, allowing doctors to clearly see the outlines of the intestines, stomach, and esophagus. However, its use in imaging the kidneys is not as common or straightforward.
How Barium Sulfate Works in Imaging
The primary function of barium sulfate in imaging is to enhance the contrast of the areas being scanned, providing clearer and more detailed images. This helps doctors identify abnormalities such as tumors, blockages, or inflammation within the digestive system. However, because barium sulfate is not absorbed by the body, it doesn’t circulate through the bloodstream like other contrast agents used in kidney imaging, such as iodine-based contrast agents used in CT scans or MRIs.
Can Barium Sulfate Be Used to Check Kidney Function?
Barium sulfate is not typically used to check kidney function directly. It is designed to enhance imaging of the gastrointestinal tract, not the kidneys or urinary system. While it may be used in imaging studies that involve the abdomen or pelvic area, its primary purpose is not to assess the kidneys themselves. To evaluate kidney function, different types of tests and imaging procedures are used.
Tests for Kidney Function
Kidney function is usually assessed through a combination of blood tests, urine tests, and specific imaging techniques. Here are some of the most common methods:
1. Blood Tests (Creatinine and GFR)
One of the most important tests for kidney function is the measurement of creatinine levels in the blood. Elevated creatinine levels can indicate that the kidneys are not functioning properly. The Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) is calculated using blood creatinine levels and other factors like age, sex, and race. A low GFR may signal kidney disease or dysfunction.
2. Urinalysis
Urinalysis is a routine test used to check for signs of kidney problems. This test can identify the presence of protein, blood, or other substances in the urine that could suggest kidney damage or disease.
3. Ultrasound Imaging
Kidney ultrasounds use sound waves to create images of the kidneys, helping doctors check for issues such as cysts, tumors, or blockages in the urinary system. It is a non-invasive and effective way to visualize kidney structure.
4. CT and MRI Scans
While barium sulfate is not typically used for kidney imaging, advanced imaging techniques like CT and MRI scans with iodine-based contrast agents can help evaluate the kidneys' structure and function. These scans provide more detailed images of the kidneys and can reveal issues like kidney stones, infections, or tumors.
Why Isn’t Barium Sulfate Used for Kidney Imaging?
Barium sulfate is designed to work by highlighting areas that contain soft tissue, such as the digestive organs, but it does not highlight the kidneys or urinary system in the same way. While it can be used to visualize the surrounding structures, it doesn’t provide detailed information about the kidneys themselves or their ability to filter waste from the blood. Therefore, it is not suitable for assessing kidney function directly.
Alternative Imaging Techniques for Kidney Health
There are several imaging techniques used specifically for checking kidney health. These methods can provide detailed information about both kidney structure and function:
1. Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP)
An intravenous pyelogram is an X-ray-based test that involves injecting a contrast dye into a vein. The dye travels through the bloodstream to the kidneys and urinary tract, where it highlights any blockages, stones, or other abnormalities. This procedure can help doctors assess kidney function and structure.
2. Renal Scintigraphy
Renal scintigraphy is a type of nuclear medicine scan that uses a radioactive tracer to evaluate kidney function. It can help doctors measure the blood flow to the kidneys, as well as their filtration ability, and is often used to diagnose conditions like chronic kidney disease or kidney failure.
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) with Contrast
MRI scans, when combined with special contrast agents, can provide highly detailed images of the kidneys. Unlike CT scans, MRI uses magnets and radio waves, making it a great option for patients who need an alternative to radiation-based imaging.
Conclusion: The Role of Barium Sulfate in Kidney Imaging
While barium sulfate plays an important role in gastrointestinal imaging, it is not used to directly assess kidney function. To evaluate kidney health, other diagnostic tests and imaging procedures are necessary. Whether you are undergoing a routine checkup or dealing with kidney-related concerns, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider about the best testing options available to ensure optimal kidney health and early detection of any issues.




 Robert B Larson, LPN, JD - Dental Attorney4.0 (5 review)
Robert B Larson, LPN, JD - Dental Attorney4.0 (5 review) HealthPartners Dental Clinic Woodbury2.0 (24 review)
HealthPartners Dental Clinic Woodbury2.0 (24 review) Dental Faculty Practice3.0 (37 review)
Dental Faculty Practice3.0 (37 review) High Tide Dental- Dr. Lucas Homicz, DDS5.0 (150 review)
High Tide Dental- Dr. Lucas Homicz, DDS5.0 (150 review) Kid's Choice Dental - Federal Way4.0 (790 review)
Kid's Choice Dental - Federal Way4.0 (790 review) OM3 Oral Maxillofacial & Implant Surgery3.0 (33 review)
OM3 Oral Maxillofacial & Implant Surgery3.0 (33 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile