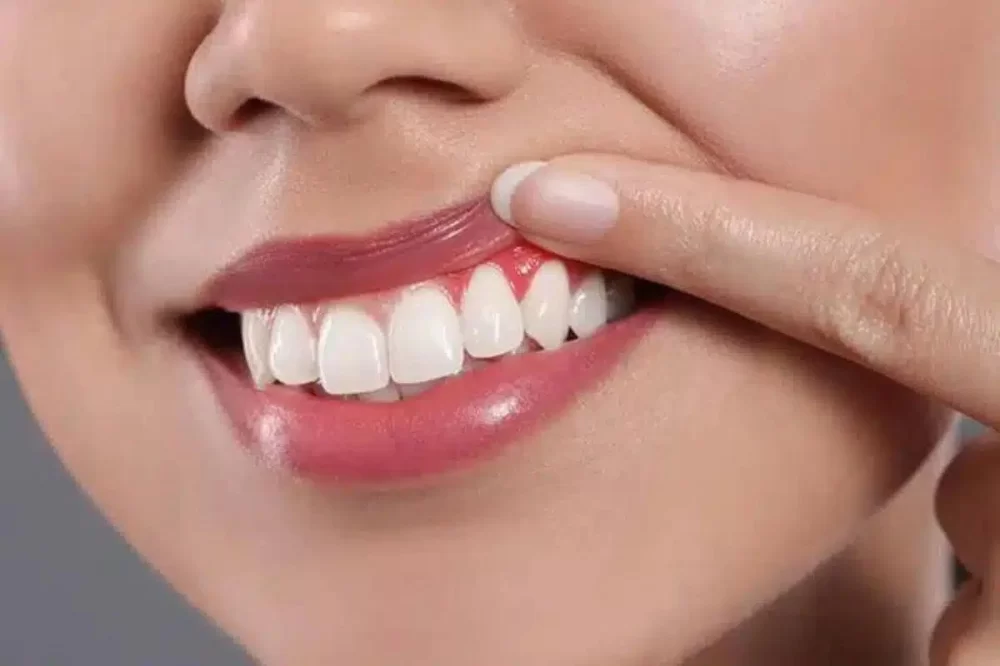

- Understanding the Link Between Gum Disease and Heart Health
- How Gum Disease Can Affect Heart Health
- Real-Life Examples of Oral Health Impact on Cardiovascular Problems
- Preventive Measures and Importance of Professional Dental Care
- Why Dentistry Toothtruth Can Help You Maintain Both Oral and Heart Health
1. Understanding the Link Between Gum Disease and Heart Health
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a chronic infection that affects the gums and surrounding tissues supporting your teeth. While many people consider it a purely dental issue, research increasingly shows that the impact of gum disease extends far beyond the mouth, potentially contributing to serious heart problems. So, can gum disease cause heart problems? The answer is complex but worth understanding.
Periodontal disease causes inflammation and allows harmful bacteria to enter the bloodstream. This systemic inflammation is believed to increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes. Medical studies have found that individuals with severe gum disease often have a higher incidence of clogged arteries, heart attacks, and other heart conditions compared to those with healthy gums.
It’s important to highlight that gum disease doesn’t directly “cause” heart problems in a simple cause-and-effect manner. Instead, it is a significant risk factor that exacerbates other underlying conditions, especially in people with existing heart health concerns.
1.1 The Science Behind the Connection
The bacteria from infected gums can travel through the bloodstream and attach to fatty plaques in the coronary arteries, contributing to clot formation. This can lead to restricted blood flow or even heart attacks. Additionally, the body’s immune response to periodontal infection causes widespread inflammation, which may further damage blood vessels and accelerate heart disease progression.
1.2 Common Risk Factors Shared
It’s also worth noting that gum disease and heart disease share many common risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, poor diet, and age. This overlap makes maintaining good oral hygiene even more critical for people with cardiovascular risk factors.
2. How Gum Disease Can Affect Heart Health
Gum disease develops silently over months or even years. Early signs include bleeding gums, bad breath, and gum recession. Left untreated, it progresses to periodontitis, causing irreversible damage to gums and supporting bone.
Once harmful bacteria breach the gum barrier, they trigger inflammatory responses not just locally but throughout the body. This chronic inflammation is harmful to blood vessels, contributing to atherosclerosis—the buildup of plaques in arteries. Over time, this process can impair the heart’s ability to function properly, leading to increased risk of heart attacks or stroke.
Furthermore, studies suggest a two-way relationship: heart disease may also impair blood flow to gum tissues, worsening gum disease severity. This reciprocal effect means managing gum health becomes crucial to support overall cardiovascular well-being.
2.1 The Role of Inflammation
Inflammation is the body’s natural defense, but chronic inflammation caused by persistent gum infection turns destructive. It raises levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), an inflammatory marker linked to heart disease risk. Monitoring and controlling inflammation through dental care and lifestyle changes can reduce cardiovascular risks.
2.2 Impact on Blood Pressure and Endothelial Function
Emerging research shows that gum disease may also influence blood pressure control and the health of the endothelium—the inner lining of blood vessels. Poor endothelial function is a key early step in heart disease development.
3. Real-Life Examples of Oral Health Impact on Cardiovascular Problems
Consider the story of John, a 52-year-old man with a history of hypertension and smoking. John neglected his oral health for years, experiencing frequent gum bleeding and discomfort. After a mild heart attack, his cardiologist asked about his dental care habits, highlighting the connection between his periodontal disease and heart condition. With professional guidance, John committed to improving his oral hygiene and underwent periodontal treatment, which helped reduce his systemic inflammation and contributed to better heart health management.
This case is not unique. Many patients with cardiovascular diseases report improvement in their symptoms after addressing their gum disease. Such real-life examples demonstrate the importance of recognizing oral health as an integral part of overall wellness.
Moreover, public health studies in communities with high rates of untreated gum disease show correspondingly elevated levels of heart disease, underscoring a significant public health concern.
4. Preventive Measures and Importance of Professional Dental Care
Prevention is the best strategy to reduce the risk of gum disease impacting heart health. Good oral hygiene practices such as regular brushing, flossing, and routine dental visits are essential. Early diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease can prevent the progression of inflammation and bacterial spread.
Regular dental cleanings and check-ups allow for removal of plaque and tartar buildup, stopping gum disease in its tracks. For those with cardiovascular risks, informing your healthcare providers about your oral health status ensures coordinated care and better management of both conditions.
4.1 Lifestyle Choices Matter
Quitting smoking, maintaining a balanced diet, controlling diabetes, and managing stress all contribute to healthier gums and heart. These lifestyle adjustments enhance the immune system’s ability to fight infections and reduce chronic inflammation.
4.2 When to Seek Help
If you notice persistent gum bleeding, swelling, or pain, it’s time to consult a dental professional. Early intervention can save not only your smile but also potentially reduce your risk of serious heart problems.
5. Why Dentistry Toothtruth Can Help You Maintain Both Oral and Heart Health
Maintaining oral health is more than just cosmetic—it’s a vital step toward protecting your heart. At Dentistry Toothtruth, we understand the deep connection between gum disease and heart problems. Our experienced dental team provides comprehensive periodontal care tailored to your needs, helping you control gum disease and lower cardiovascular risks.
We offer personalized advice, the latest treatments, and ongoing support to ensure your oral health positively contributes to your overall well-being. Whether you are seeking preventive care or managing existing conditions, Dentistry Toothtruth is your trusted partner on the journey to better health.
Remember, taking care of your gums today could be one of the most important steps you take to protect your heart tomorrow.







 North Columbus Dental Group5.0 (2 review)
North Columbus Dental Group5.0 (2 review) Monarch Dental & Orthodontics4.0 (557 review)
Monarch Dental & Orthodontics4.0 (557 review) Bob and Peg's Dental5.0 (4 review)
Bob and Peg's Dental5.0 (4 review) Corner Dentistry4.0 (42 review)
Corner Dentistry4.0 (42 review) Midlothian Family Dentistry4.0 (649 review)
Midlothian Family Dentistry4.0 (649 review) River Run Dental4.0 (356 review)
River Run Dental4.0 (356 review) The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile